Population Structure, Stratification, and Introgression of Human Structural Variation
- PMID: 32531199
- PMCID: PMC7369638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.024
Population Structure, Stratification, and Introgression of Human Structural Variation
Abstract
Structural variants contribute substantially to genetic diversity and are important evolutionarily and medically, but they are still understudied. Here we present a comprehensive analysis of structural variation in the Human Genome Diversity panel, a high-coverage dataset of 911 samples from 54 diverse worldwide populations. We identify, in total, 126,018 variants, 78% of which were not identified in previous global sequencing projects. Some reach high frequency and are private to continental groups or even individual populations, including regionally restricted runaway duplications and putatively introgressed variants from archaic hominins. By de novo assembly of 25 genomes using linked-read sequencing, we discover 1,643 breakpoint-resolved unique insertions, in aggregate accounting for 1.9 Mb of sequence absent from the GRCh38 reference. Our results illustrate the limitation of a single human reference and the need for high-quality genomes from diverse populations to fully discover and understand human genetic variation.
Keywords: Human Genome Diversity Project; archaic introgression; denisova; diverse genomes; neanderthal; runaway duplications; sequences missing from the reference; structural variation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests M.E.H. is a co-founder of, director of, share-holder in, and consultant to Congenica.
Figures

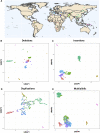


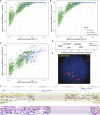






Comment in
-
A Worldwide Map of Human Structural Variants.Trends Genet. 2020 Oct;36(10):722-725. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Trends Genet. 2020. PMID: 32690317
References
-
- Akay A., Di Domenico T., Suen K.M., Nabih A., Parada G.E., Larance M., Medhi R., Berkyurek A.C., Zhang X., Wedeles C.J. The helicase aquarius/EMB-4 is required to overcome intronic barriers to allow nuclear RNAi pathways to heritably silence transcription. Dev. Cell. 2017;42:241–255.e6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akkaya M., Barclay A.N. How do pathogens drive the evolution of paired receptors? Eur. J. Immunol. 2013;43:303–313. - PubMed
-
- Angata T., Hayakawa T., Yamanaka M., Varki A., Nakamura M. Discovery of Siglec-14, a novel sialic acid receptor undergoing concerted evolution with Siglec-5 in primates. FASEB J. 2006;20:1964–1973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

