Senescent Cells: Emerging Targets for Human Aging and Age-Related Diseases
- PMID: 32531228
- PMCID: PMC7649645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.03.008
Senescent Cells: Emerging Targets for Human Aging and Age-Related Diseases
Abstract
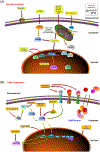
Aging is a major risk factor for numerous human pathologies, including cardiovascular, metabolic, musculoskeletal, and neurodegenerative conditions and various malignancies. While our understanding of aging is far from complete, recent advances suggest that targeting fundamental aging processes can delay, prevent, or alleviate age-related disorders. Cellular senescence is physiologically beneficial in several contexts, but it has causal roles in multiple chronic diseases. New studies have illustrated the promising feasibility and safety to selectively ablate senescent cells from tissues, a therapeutic modality that holds potential for treating multiple chronic pathologies and extending human healthspan. Here, we review molecular links between cellular senescence and age-associated complications and highlight novel therapeutic avenues that may be exploited to target senescent cells in future geriatric medicine.
Keywords: SASP; cellular senescence; clinical trials; geroscience; senolytics.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclaimer Statement
J.L.K. and T.T. have a financial interest related to this research. Patents on senolytic drugs are held by the Mayo Clinic. This research has been reviewed by the Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest Review Board and was conducted in compliance with Mayo Clinic Conflict of Interest policies.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

