Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32531256
- PMCID: PMC7283076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.017
Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
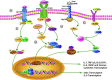
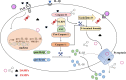
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the virus designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has spread widely throughout the world. Despite the strict global outbreak management and quarantine measures that have been implemented, the incidence of COVID-19 continues to rise, resulting in more than 290,000 deaths and representing an extremely serious threat to human life and health. The clinical symptoms of the affected patients are heterogeneous, ranging from mild upper respiratory symptoms to severe pneumonitis and even acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or death. Systemic immune over activation due to SARS-CoV-2 infection causes the cytokine storm, which is especially noteworthy in severely ill patients with COVID-19. Pieces of evidence from current studies have shown that the cytokine storm may be an important factor in disease progression, even leading to multiple organ failure and death. This review provides an overview of the knowledge on the COVID-19 epidemiological profile, the molecular mechanisms of the SARS-CoV-2-induced cytokine storm and immune responses, the pathophysiological changes that occur during infection, the main antiviral compounds used in treatment strategies and the potential drugs for targeting cytokines, this information is presented to provide valuable guidance for further studies and for a therapeutic reduction of this excessive immune response.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical manifestations; Coronavirus; Cytokine storm; Pneumonia; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports, https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio..., 2020 (accessed 15 May 2020).
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, Outbreak report, http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202005/d2059dd74f8e4e469c1ad3fb6cf0e3af.s..., 2020 (accessed 15 May 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

