The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects
- PMID: 32532960
- PMCID: PMC7292831
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x
The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects
Abstract
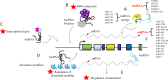
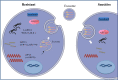
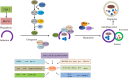
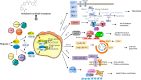
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor capable of facilitating apoptosis, mitigating angiogenesis and suppressing tumor cell proliferation. In late-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), sorafenib is currently an effective first-line therapy. Unfortunately, the development of drug resistance to sorafenib is becoming increasingly common. This study aims to identify factors contributing to resistance and ways to mitigate resistance. Recent studies have shown that epigenetics, transport processes, regulated cell death, and the tumor microenvironment are involved in the development of sorafenib resistance in HCC and subsequent HCC progression. This study summarizes discoveries achieved recently in terms of the principles of sorafenib resistance and outlines approaches suitable for improving therapeutic outcomes for HCC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Torre LA, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301–1314. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Wang H. Heterogeneity of liver cancer and personalized therapy. Cancer Lett. 2016;379:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

