Functional annotation of rare structural variation in the human brain
- PMID: 32533064
- PMCID: PMC7293301
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16736-1
Functional annotation of rare structural variation in the human brain
Abstract
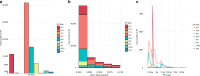
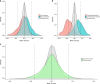
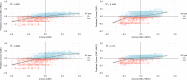
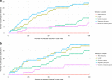
Structural variants (SVs) contribute to many disorders, yet, functionally annotating them remains a major challenge. Here, we integrate SVs with RNA-sequencing from human post-mortem brains to quantify their dosage and regulatory effects. We show that genic and regulatory SVs exist at significantly lower frequencies than intergenic SVs. Functional impact of copy number variants (CNVs) stems from both the proportion of genic and regulatory content altered and loss-of-function intolerance of the gene. We train a linear model to predict expression effects of rare CNVs and use it to annotate regulatory disruption of CNVs from 14,891 independent genome-sequenced individuals. Pathogenic deletions implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders show significantly more extreme regulatory disruption scores and if rank ordered would be prioritized higher than using frequency or length alone. This work shows the deleteriousness of regulatory SVs, particularly those altering CTCF sites and provides a simple approach for functionally annotating the regulatory consequences of CNVs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR. Structural variation in the human genome and its role in disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010;61:437–455. - PubMed
-
- Weischenfeldt J, Symmons O, Spitz F, Korbel JO. Phenotypic impact of genomic structural variation: insights from and for human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013;14:125–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32 LM012412/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109897/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- L30 NS093200/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201400099C/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH115957/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG049688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109677/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD081256/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- ZIC MH002903/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111776/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS093200/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM127087/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD096326/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

