Resident mesenchymal vascular progenitors modulate adaptive angiogenesis and pulmonary remodeling via regulation of canonical Wnt signaling
- PMID: 32533805
- PMCID: PMC7496763
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202000629R
Resident mesenchymal vascular progenitors modulate adaptive angiogenesis and pulmonary remodeling via regulation of canonical Wnt signaling
Abstract
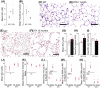
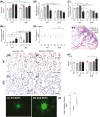
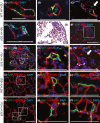
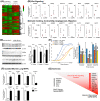
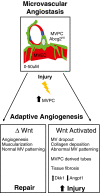
Adaptive angiogenesis is necessary for tissue repair, however, it may also be associated with the exacerbation of injury and development of chronic disease. In these studies, we demonstrate that lung mesenchymal vascular progenitor cells (MVPC) modulate adaptive angiogenesis via lineage trace, depletion of MVPC, and modulation of β-catenin expression. Single cell sequencing confirmed MVPC as multipotential vascular progenitors, thus, genetic depletion resulted in alveolar simplification with reduced adaptive angiogenesis. Following vascular endothelial injury, Wnt activation in MVPC was sufficient to elicit an emphysema-like phenotype characterized by increased MLI, fibrosis, and MVPC driven adaptive angiogenesis. Lastly, activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling skewed the profile of human and murine MVPC toward an adaptive phenotype. These data suggest that lung MVPC drive angiogenesis in response to injury and regulate the microvascular niche as well as subsequent distal lung tissue architecture via Wnt signaling.
Keywords: Wnt signaling; adaptive angiogenesis; emphysema; mesenchymal vascular progenitor cell; microvascular niche.
© 2020 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Sabit R, Bolton CE, Edwards PH, et al. Arterial stiffness and osteoporosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:1259‐1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL116597/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116597/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD073063/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 BX003841/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- UL1 TR000445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL136449/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095797/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000445-06/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL130595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136449/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126732/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

