Health-Related Quality of Life in MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as Initial Therapy in HR+, HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32536013
- PMCID: PMC7485333
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2020-0084
Health-Related Quality of Life in MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib plus an Aromatase Inhibitor as Initial Therapy in HR+, HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: MONARCH 3, a phase III trial (NCT02246621) of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC), previously demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival in patients receiving abemaciclib plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI). This study evaluated patient-reported outcomes, including global health-related quality of life (HRQoL), functioning, and symptoms.
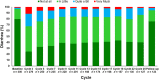
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned 2:1 to receive abemaciclib (150 mg twice daily; n = 328) or placebo (n = 165), plus 1 mg anastrozole or 2.5 mg letrozole daily. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 and Breast Cancer-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire HRQoL instruments were administered at baseline, every two cycles during cycles 2 through 19 (each cycle being 28 days), every three cycles thereafter, and once at a short-term posttherapy follow-up visit (approximately 30 days after discontinuation). Longitudinal mixed regression and Cox proportional hazards models evaluated postbaseline change and time to sustained deterioration (TTSD), respectively.
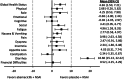
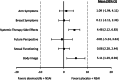
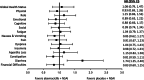
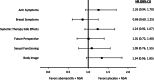
Results: Baseline scores were similar between treatment arms. Although select scores statistically favored the placebo arm, global HRQoL, most symptoms, and functioning scales did not meet the threshold for clinically meaningful differences between treatment arms. Only diarrhea favored the placebo arm with statistically and clinically meaningful differences. There were no TTSD differences between treatment arms for global HRQoL, most symptoms (except diarrhea), or functioning.
Conclusion: Over a 2-year period, there were no clinically meaningful differences in global HRQoL, functioning, and most symptoms for patients receiving abemaciclib plus NSAI compared with NSAI alone. Only diarrhea favored the placebo arm, consistent with prior safety data, which has been shown to be manageable and reversible. Combined with clinical efficacy, results support treatment with abemaciclib plus NSAI for postmenopausal women with HR+, HER2- ABC.
Implications for practice: The addition of abemaciclib to a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) was not associated with a clinically meaningful detriment in patient-reported global health-related quality of life, functioning, and most symptoms in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC). Prior studies have also demonstrated clinical efficacy of abemaciclib plus NSAI compared with NSAI alone, including improved progression-free survival and objective response rate. These results also complement previously reported toxicity data, as measured by investigator-assessed adverse events. Taken together, these results support treatment with abemaciclib plus NSAI for postmenopausal women with HR+, HER2- ABC.
Keywords: Abemaciclib; Advanced breast cancer; Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor; Health-related quality of life; Patient-reported outcomes.
© 2020 The Authors. The Oncologist published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-Related Quality of Life in MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant in Hormone Receptor-Positive, HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer After Endocrine Therapy.Oncologist. 2020 Feb;25(2):e243-e251. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0551. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32043763 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abemaciclib plus a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor as initial therapy for HR+, HER2- advanced breast cancer: final overall survival results of MONARCH 3.Ann Oncol. 2024 Aug;35(8):718-727. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.04.013. Epub 2024 May 8. Ann Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38729566 Clinical Trial.
-
Abemaciclib plus non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: Final results of the randomized phase III MONARCH plus trial.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Jun 20;138(12):1477-1486. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003151. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39385327 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Development of CDK4 & 6 Inhibitor Abemaciclib in Breast Cancer].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2021 Dec;48(12):1475-1483. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2021. PMID: 34911915 Review. Japanese.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Abemaciclib in Combination With Endocrine Therapy for HR+/HER2- Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jan 1;48(1):6-15. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000001143. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Am J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39249111
Cited by
-
Health-related quality of life in premenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer treated with ribociclib plus endocrine therapy: results from a phase III randomized clinical trial (MONALEESA-7).Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Jul 26;12:1758835920943065. doi: 10.1177/1758835920943065. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32782490 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life with ribociclib versus abemaciclib as first-line treatment of HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: a matching-adjusted indirect comparison.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Feb 24;15:17588359231152843. doi: 10.1177/17588359231152843. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36861085 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Treatment for Breast Cancer Patients Revisited-History, Standard of Care, and Possibilities of Improvement.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;13(22):5643. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225643. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Healthcare Resource Utilization and Cost Comparison Between Palbociclib, Abemaciclib, and Ribociclib Among Patients with HR+/HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2025 Mar 26;17:247-264. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S496100. eCollection 2025. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2025. PMID: 40165979 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Reported Outcomes Predict Progression-Free Survival of Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with Abemaciclib.Oncologist. 2021 Jul;26(7):562-568. doi: 10.1002/onco.13806. Epub 2021 May 11. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 33914991 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Gradishar W, Salemo KE. NCCN guidelines update: Breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2016;14(suppl 5):641–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

