Tests in short supply? Try group testing
- PMID: 32536952
- PMCID: PMC7283891
- DOI: 10.1111/1740-9713.01399
Tests in short supply? Try group testing
Abstract
Christopher R. Bilder, Peter C. Iwen, Baha Abdalhamid, Joshua M. Tebbs and Christopher S. McMahan explain how, by pooling specimens, testing capacity for SARS-CoV-2 can be increased.
© 2020 The Royal Statistical Society.
Figures
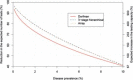

References
-
- Dorfman R. (1943) The detection of defective members of large populations. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 14, 436–440.
-
- Lewis, J., Lockary, V. and Kobic, S. (2012) Cost savings and increased efficiency using a stratified specimen pooling strategy for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 39, 46–48. - PubMed
-
- Græsb⊘ll, K., Andresen, L., Halasa, T. and Toft, N. (2017) Opportunities and challenges when pooling milk samples using ELISA. Preventative Veterinary Medicine, 139, 93–98. - PubMed
-
- Salzer, E., Nixon, E., Drewes, G., Reinhard, F., Bergamini, G. and Rau, C. (2016) Screening pools of compounds against multiple endogenously expressed targets in a chemoproteomics binding assay. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 21, 133–142. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
