Rosuvastatin protects against endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro and alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 32537013
- PMCID: PMC7282009
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.8733
Rosuvastatin protects against endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro and alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
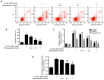
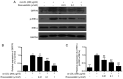
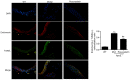
The development of abnormal lipid-induced atherosclerosis is initiated with endothelial cell apoptosis. Vascular endothelial cells possess highly developed endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which is involved in lipid metabolism, indicating that ER stress may contribute chiefly to the induction of endothelial cell apoptosis. Based on its ability to reduce cholesterol levels, rosuvastatin may play an endothelial and vascular protective role by regulating ER stress. In the present study, the involvement of the inhibition of the ER stress-induced endothelial injury was investigated in combination with the lipid lowering effects of rosuvastatin. This compound can be used to inhibit cholesterol synthesis in atherosclerosis. Rosuvastatin decreased the apoptotic rates of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) that had been stimulated with ox-low density lipoprotein (LDL) in vitro and repressed the mRNA levels of CHOP, sXBP1 and caspase-12, and decreased caspase-12 activity, as well as the content of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), phosphorylated (p)-protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK), p-inositol-requiring protein 1α (IRE1α) and p-eIF2α proteins. In addition, ApoE-/- mice were fed with atherogenic chow for 8 weeks for atherosclerosis induction and rosuvastatin was provided by intragastric administration for an additional 4 weeks. Subsequently, the atherosclerotic plaque formation in the aorta was evaluated by Oil Red O and hematoxylin and eosin staining, and the serum LDL, high-density lipoprotein, total cholesterol (TC) and triacylglycerol (TG) levels were measured. In addition, the induction of apoptosis of endothelial cells and the expression levels of GRP78, p-PERK, p-IRE1α and p-eIF2α were assessed in the aorta. Rosuvastatin repressed atherosclerotic plaque formation and endothelial apoptosis in the aorta and decreased LDL and TG levels in the serum, as determined by in vivo results. Furthermore, it downregulated the expression levels of protein chaperone GRP78, p-PERK, p-IRE1α and p-eIF2α in the aortic intima. The data indicated that rosuvastatin could protect HUVECs from ER stress-induced apoptosis triggered by oxidized LDL. It could also inhibit atherosclerosis formation in ApoE-/- mice aorta by regulating the PERK/eIF2α/C/EBPα-homologous protein and IRE1α/sXBP1 signaling pathways. Taken collectively, the present study demonstrated the preventive and therapeutic effects of rosuvastatin in protecting from the development of endothelial cell dysfunction diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; endoplasmic reticulum stress; endothelial cell apoptosis; rosuvastatin.
Copyright: © Geng et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of PERK/eIF2α/CHOP Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway in Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein Mediated Induction of Endothelial Apoptosis.Biomed Environ Sci. 2016 Dec;29(12):868-876. doi: 10.3967/bes2016.116. Biomed Environ Sci. 2016. PMID: 28081747
-
Hypermethylation of the CTRP9 promoter region promotes Hcy induced VSMC lipid deposition and foam cell formation via negatively regulating ER stress.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 9;13(1):19438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46981-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37945738 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Simvastatin on Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Vascular Endothelial Cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Apr 20;131(8):950-955. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.229891. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29664056 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cardiovascular Disease and Exercise.Int J Vasc Med. 2017;2017:2049217. doi: 10.1155/2017/2049217. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Int J Vasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28875043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Macrophages: The Vicious Circle of Lipid Accumulation and Pro-Inflammatory Response.Biomedicines. 2020 Jul 13;8(7):210. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8070210. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32668733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical study of different doses of atorvastatin combined with febuxostat in patients with gout and carotid atherosclerosis.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Sep-Oct;36(6):1334-1338. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.6.2945. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32968404 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-129 and miR-342 derived from intermittent hypoxia-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells inhibit the eIF2α/ATF4 axis from preventing calcified aortic valvular disease.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec;17(4):1449-1467. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00785-4. Epub 2023 Oct 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37812275 Free PMC article.
-
Graft protective effects and donor-specific antibody suppression by CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell induced by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor rosuvastatin in a murine heart transplant model.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Jun 25;19(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02888-4. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38918849 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted delivery of rosuvastatin enhances treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia-induced atherosclerosis using macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Sep;14(9):100937. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Jan 13. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39345941 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin protects PC12 cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1189. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10623. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34475979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hald EM, Lijfering WM, Mathiesen EB, Johnsen SH, Løchen ML, Njølstad I, Wilsgaard T, Rosendaal FR, Brækkan SK, Hansen JB. Carotid atherosclerosis predicts future myocardial infarction but not venous thromboembolism: The Tromso study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:226–230. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302162. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
