Identification of hub genes associated with RNAi-induced silencing of XIAP through targeted proteomics approach in MCF7 cells
- PMID: 32537125
- PMCID: PMC7291505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-020-00437-9
Identification of hub genes associated with RNAi-induced silencing of XIAP through targeted proteomics approach in MCF7 cells
Abstract
Background: The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is the most potent caspase inhibitor of the IAP family in apoptosis pathway. This study aims to identify the molecular targets of XIAP in human breast cancer cells exposed to XIAP siRNA by proteomics screening. The expression of XIAP was reduced in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by siRNA. Cell viability and the mRNA expression level of this gene were evaluated by MTS and quantitative real-time PCR procedures, respectively. Subsequently, the XIAP protein level was visualized by Western blotting and analyzed by two-dimensional (2D) electrophoresis and LC-ESI-MS/MS.
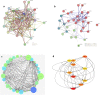
Results: Following XIAP silencing, cell proliferation was reduced in XIAP siRNA transfected cells. The mRNA transcription and protein expression of XIAP were decreased in cells exposed to XIAP siRNA than si-NEG. We identified 30 proteins that were regulated by XIAP, of which 27 down-regulated and 3 up-regulated. The most down-regulated proteins belonged to the Heat Shock Proteins family. They participate in cancer related processes including apoptosis and MAPK signaling pathway. Reduced expression of HSP90B1 was associated with apoptosis induction by androgen receptor and prostate specific antigen. Suppression of XIAP resulted in the enhancement of GDIB, ENO1, and CH60 proteins expression. The network analysis of XIAP-regulated proteins identified HSPA8, HSP90AA1, ENO1, and HSPA9 as key nodes in terms of degree and betweenness centrality methods.
Conclusions: These results suggested that XIAP may have a number of biological functions in a diverse set of non-apoptotic signaling pathways and may provide an insight into the biomedical significance of XIAP over-expression in MCF-7 cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast cancer; Molecular targets; Proteomics; RNA interference; XIAP.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Hickman JA. Apoptosis and tumourigenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12(1):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Uren AG, Coulson EJ, Vaux DL. Conservation of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis repeat proteins (BIRPs) in viruses, nematodes, vertebrates and yeasts. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23(5):159–162. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi R, Deveraux Q, Tamm I, Welsh K, Assa-Munt N, Salvesen GS, et al. A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(14):7787–7790. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Feng Q, Kim J-M, Schneiderman D, Liston P, Li M, et al. Human Ovarian Cancer and Cisplatin Resistance: possible Role of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins** This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-15691), the University of Ottawa-Industry Grants Program, and the Ottawa Civic Hospital Foundation. Endocrinology. 2001;142(1):370–380. - PubMed
-
- Satoh K, Kaneko K, Hirota M, Masamune A, Satoh A, Shimosegawa T. Expression of survivin is correlated with cancer cell apoptosis and is involved in the development of human pancreatic duct cell tumors. Cancer. 2001;92(2):271–278. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

