Building a Multidisciplinary Comprehensive Academic Lymphedema Program
- PMID: 32537334
- PMCID: PMC7253282
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002670
Building a Multidisciplinary Comprehensive Academic Lymphedema Program
Abstract
Lymphedema is a debilitating clinical condition predominantly affecting survivors of cancer. It adversely affects patients' quality of life and results in substantial cost burdens to both patients and the healthcare system. Specialist lymphedema care is optimally provided within integrated clinical programs that align the necessary specialties to provide patient-focused, multidisciplinary, structured, and coordinated care. This article examines our experience building a specialist lymphedema academic program.
Methods: We describe the critical components necessary for constructing a multidisciplinary comprehensive academic lymphedema program. Furthermore, lessons learned from our experience building a successful lymphedema program are discussed.
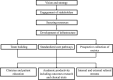
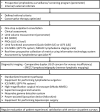
Results: Building a comprehensive academic lymphedema program requires institutional support and engagement of stakeholders to establish the necessary infrastructure for comprehensive patient care. This includes the infrastructure for outpatient clinical assessment, diagnostic investigations, radiological imaging, collection of outcomes metrics, non-surgical treatment delivered by lymphedema-specialist therapists, surgical procedures using specialized equipment, and integration of an outpatient framework for comprehensive patient evaluation during follow-up at standardized time intervals.
Conclusions: This article examines our experience building a multidisciplinary comprehensive academic lymphedema program and provides a structured roadmap to benefit others that are embarking on this mission.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Moffatt CJ, Franks PJ, Doherty DC, et al. Lymphoedema: an underestimated health problem. QJM. 2003;96:731–738. - PubMed
-
- Rockson SG, Rivera KK. Estimating the population burden of lymphedema. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1131:147–154. - PubMed
-
- Cormier JN, Askew RL, Mungovan KS, et al. Lymphedema beyond breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cancer-related secondary lymphedema. Cancer. 2010;116:5138–5149. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources