Lung Ultrasound Score Predicts the Extravascular Lung Water Content in Low-Birth-Weight Neonates with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- PMID: 32538377
- PMCID: PMC7315804
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.921671
Lung Ultrasound Score Predicts the Extravascular Lung Water Content in Low-Birth-Weight Neonates with Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Abstract
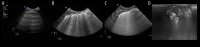
BACKGROUND Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a common congenital cardiac abnormality in premature infants. In low-birth-weight infants weighing less than 2500 g, if the PDA continues to open, abnormal circulation hemodynamics and pulmonary edema may occur. This study aimed to investigate the role of lung ultrasound score in the assessment of pulmonary edema in low-weight neonates with PDA. MATERIAL AND METHODS Two hundred and twenty-one neonates with low birth weight were selected as the subjects, children with PDA as the observation group, and children with closed ductus arteriosus as the control group. On the fourth postnatal day, lung ultrasound examination and 6-segment lung ultrasound scoring were performed. RESULTS All 221 infants (94 in the observation group, 127 controls) underwent ultrasound examinations of the lungs. Intergroup differences in gestational age, birth weight, length of hospital stay, and left ventricular ejection fraction were not statistically significant. There was a significant difference in lung ultrasound score (t=0.005, P=0.000) and aortic root ratio to left atrial (t=0.085, P=0.000), which was negatively correlated with gestational age (r=-0.235, P=0.000) and positively correlated with PDA diameter (r=0.261, P=0.011). CONCLUSIONS Low-birth-weight children often have PDA. Its continued opening changes the circulation hemodynamics in children. Lung ultrasound score can semi-quantitatively evaluate the extravascular lung water content, identifying the need to intervene and follow up the hemodynamic significance of PDA over time.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bedside cardiopulmonary ultrasonography evaluates lung water content in very low-weight preterm neonates with patent ductus arteriosus.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Mar 16;9(8):1827-1834. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i8.1827. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33748231 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of color Doppler echocardiographic findings in premature newborns with patent ductus arteriosus.Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1997 Mar-Apr;38(2):104-10. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1997. PMID: 9151462
-
Lung ultrasound score in the decision of patent ductus arteriosus closure in neonates.J Clin Ultrasound. 2024 May;52(4):415-425. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23653. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Clin Ultrasound. 2024. PMID: 38385619
-
Hemodynamic assessment of the patent ductus arteriosus: Beyond ultrasound.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018 Aug;23(4):239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018. PMID: 29730050 Review.
-
Patent ductus arteriosus in micropreemies and full-term infants: the relative merits of surgical ligation versus indomethacin treatment.J Pediatr Surg. 2003 Mar;38(3):492-6. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2003.50086. J Pediatr Surg. 2003. PMID: 12632374 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of lung ultrasound score with large patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates during the transitional period.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 May 20;184(6):348. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06186-6. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40392344
-
Cardiopulmonary Ultrasound-Guided Treatment of Premature Infants with Respiratory Failure and Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Randomized, Controlled Trial.Indian J Pediatr. 2023 Nov;90(11):1103-1109. doi: 10.1007/s12098-023-04489-w. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Indian J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36952111 Clinical Trial.
-
The Predictive Value of Lung Ultrasound Score on Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus among Neonates ≤25 Weeks.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 4;13(13):2263. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132263. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443657 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of Lung Ultrasound Score in Neonatology.Front Pediatr. 2022 May 11;10:791664. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.791664. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35633958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of different types of ultrasound probes for lung ultrasound in neonates-A prospective randomized comparison study.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 3;19(7):e0306472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306472. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38959257 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Benitz WE Committee on Fetus and Newborn, American Academy of Pediatrics. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1) - PubMed
-
- Almeida-Jones M, Tang NY, Reddy A, Zahn E. Overview of transcatheter patent ductus arteriosus closure in preterm infants. Congenit Heart Dis. 2019;14(1):60–64. - PubMed
-
- Kurepa D, Zaghloul N, Watkins L, et al. Neonatal lung ultrasound exam guidelines. J Perinatol. 2017;38(1):11–22. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein DA. Current misconceptions in lung ultrasound: A short guide for experts. Chest. 2019;156(1):21–25. - PubMed
-
- De Martino L, Yousef N, Ben-Ammar R, et al. Lung ultrasound score predicts surfactant need in extremely preterm neonates. Pediatrics. 2018;142(3):e20180463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

