SUMOylation of synaptic and synapse-associated proteins: An update
- PMID: 32538470
- PMCID: PMC8218484
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.15103
SUMOylation of synaptic and synapse-associated proteins: An update
Abstract
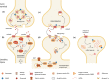
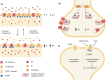
SUMOylation is a post-translational modification that regulates protein signalling and complex formation by adjusting the conformation or protein-protein interactions of the substrate protein. There is a compelling and rapidly expanding body of evidence that, in addition to SUMOylation of nuclear proteins, SUMOylation of extranuclear proteins contributes to the control of neuronal development, neuronal stress responses and synaptic transmission and plasticity. In this brief review we provide an update of recent developments in the identification of synaptic and synapse-associated SUMO target proteins and discuss the cell biological and functional implications of these discoveries.
Keywords: GTPases; SUMOylation; ion channels; synaptic plasticity; synaptic proteins.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures

References
-
- Benson, M. , Iniguez‐Lluhi, J. A. , & Martens, J. (2017). Sumo modification of ion channels. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 963, 127–141. - PubMed
-
- Benson, M. D. , Li, Q. J. , Kieckhafer, K. , Dudek, D. , Whorton, M. R. , Sunahara, R. K. , … Martens, J. R. (2007). SUMO modification regulates inactivation of the voltage‐gated potassium channel Kv1.5. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104, 1805–1810. 10.1073/pnas.0606702104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

