Layilin augments integrin activation to promote antitumor immunity
- PMID: 32539073
- PMCID: PMC7478725
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20192080
Layilin augments integrin activation to promote antitumor immunity
Abstract
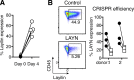
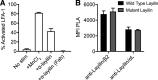
Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells mediate antitumor immune responses. However, the mechanisms by which T cells remain poised to kill cancer cells despite expressing high levels of inhibitory receptors are unknown. Here, we report that layilin, a C-type lectin domain-containing membrane glycoprotein, is selectively expressed on highly activated, clonally expanded, but phenotypically exhausted CD8+ T cells in human melanoma. Lineage-specific deletion of layilin on murine CD8+ T cells reduced their accumulation in tumors and increased tumor growth in vivo. Congruently, gene editing of LAYN in human CD8+ T cells reduced direct tumor cell killing ex vivo. On a molecular level, layilin colocalized with integrin αLβ2 (LFA-1) on T cells, and cross-linking layilin promoted the activated state of this integrin. Accordingly, LAYN deletion resulted in attenuated LFA-1-dependent cellular adhesion. Collectively, our results identify layilin as part of a molecular pathway in which exhausted or "dysfunctional" CD8+ T cells enhance cellular adhesiveness to maintain their cytotoxic potential.
© 2020 Mahuron et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: K.M. Mahuron reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; in addition, K.M. Mahuron had a patent to compositions and methods involving layilin pending. J.M. Moreau reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; in addition, J.M. Moreau had a patent to compositions and methods involving layilin pending. M.L. Pauli reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; personal fees from TRex Bio, Inc. outside the submitted work; and has been a consultant for TRex Bio, Inc. since January 2019. R.M. Feldman reported personal fees from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study and personal fees from TRex Bio, Inc. outside the submitted work. P. Mehta reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; in addition, P. Mehta had a patent to compositions and methods involving layilin pending. M.M. Lowe reported a patent to UCSF/TRex Bio, Inc. pending. A. Marson reported personal fees from Arsenal Biosciences, Spotlight Therapeutics, PACT Pharma, Trizell, Juno Therapeutics, Health Advances, Lonza, Bernstein, AbbVie, Genentech, Merck, Illumina, Arcus, Jackson Laboratories, Nanostring Technologies, GLG, and Rupert Case Management; grants from Juno Therapeutics, Epinomics, Sanofi, and Gilead; non-financial support from Illumina; grants from Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy; personal fees from AlphaSights, ALDA, and Amgen; "other" from ThermoFisher outside the submitted work; and reporting an inventorship on IP licensed to Arsenal Biosciences, Juno Therapeutics, and Fate Therapeutics. J. Wells reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study, grants from Celgene, and personal fees from Cytomix outside the submitted work. R. Jupp was an employee of TRex Bio, Inc. at the time of the study. A.I. Daud reported "other" from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; grants from Merck, BMS, Roche, and Novartis; "other" from Genentech; grants from Checkmate and Incyte; personal fees from Array; and grants from Xencor, Curis, and OncoSec outside the submitted work. M.D. Rosenblum reported grants from TRex Bio, Inc. during the conduct of the study; personal fees from TRex Bio, Inc. outside the submitted work; and had a patent to UCSF/TRex Bio, Inc. pending. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures







References
-
- Anikeeva N., Somersalo K., Sims T.N., Thomas V.K., Dustin M.L., and Sykulev Y.. 2005. Distinct role of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 in mediating effective cytolytic activity by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:6437–6442. 10.1073/pnas.0502467102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

