Curation of cancer hallmark-based genes and pathways for in silico characterization of chemical carcinogenesis
- PMID: 32539087
- PMCID: PMC7294774
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baaa045
Curation of cancer hallmark-based genes and pathways for in silico characterization of chemical carcinogenesis
Abstract
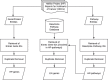
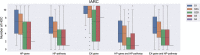
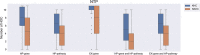
Exposure to toxic substances in the environment is one of the most important causes of cancer. However, the time-consuming process for the identification and characterization of carcinogens is not applicable to a huge amount of testing chemicals. The data gaps make the carcinogenic risk uncontrollable. An efficient and effective way of prioritizing chemicals of carcinogenic concern with interpretable mechanism information is highly desirable. This study presents a curation work for genes and pathways associated with 11 hallmarks of cancer (HOCs) reported by the Halifax Project. To demonstrate the usefulness of the curated HOC data, the interacting HOC genes and affected HOC pathways of chemicals of the three carcinogen lists from IARC, NTP and EPA were analyzed using the in silico toxicogenomics ChemDIS system. Results showed that a higher number of affected HOCs were observed for known carcinogens than the other chemicals. The curated HOC data is expected to be useful for prioritizing chemicals of carcinogenic concern. Database URL: The HOC database is available at https://github.com/hocdb-KMU-TMU/hocdb and the website of Database journal as Supplementary Data.
Keywords: cancer hallmark; curation; the Halifax Project.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
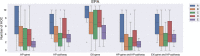
Similar articles
-
Testing the low dose mixtures hypothesis from the Halifax project.Rev Environ Health. 2020 Aug 24;35(4):333-357. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2020-0033. Print 2020 Nov 18. Rev Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 32833669 Review.
-
In vitro perturbations of targets in cancer hallmark processes predict rodent chemical carcinogenesis.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Jan;131(1):40-55. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs285. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23024176
-
Integrating AI-powered text mining from PubTator into the manual curation workflow at the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database.Database (Oxford). 2025 Feb 21;2025:baaf013. doi: 10.1093/database/baaf013. Database (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 39982792 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of specific mRNA signatures as fingerprints for carcinogenesis in mice induced by genotoxic and nongenotoxic hepatocarcinogens.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Feb;143(2):277-95. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu248. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25410580
-
Evaluation of the utility of the lifetime mouse bioassay in the identification of cancer hazards for humans.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Oct;60:550-62. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.08.020. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23954551 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutational differences between primary cancer tissue and circulating tumor cells in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):3026-3038. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-709. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39669998 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based analysis uncovers mutations altering autophagy selectivity in human cancer.Nat Commun. 2021 May 31;12(1):3258. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23539-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34059679 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Single-Atom Nanozymes Toward Environmental Pollutants: Monitoring and Control.Nanomicro Lett. 2025 Apr 28;17(1):238. doi: 10.1007/s40820-025-01734-z. Nanomicro Lett. 2025. PMID: 40293645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A gene set enrichment analysis for cancer hallmarks.J Pharm Anal. 2025 May;15(5):101065. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101065. Epub 2024 Aug 3. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 40496069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Straif K. (2008) The burden of occupational cancer. Occup. Environ. Med., 65, 787–788. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Global health risks : mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44203 (4 February 2020, date last accessed).
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2020) Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–125. IARC Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans. https://monographs.iarc.fr/agents-classified-by-the-iarc (4 February 2020, date last accessed).
-
- National Toxicology Program. (2020) 14th Report on Carcinogens https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/go/roc14 (4 February 2020, date last accessed).
-
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (2015) Evaluating pesticides for carcinogenic potential. Evaluating Pesticides for Carcinogenic Potential. https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-science-and-assessing-pesticide-risks/eval... (4 February 2020, date last accessed).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

