Why COVID-19 Silent Hypoxemia Is Baffling to Physicians
- PMID: 32539537
- PMCID: PMC7397783
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202006-2157CP
Why COVID-19 Silent Hypoxemia Is Baffling to Physicians
Abstract
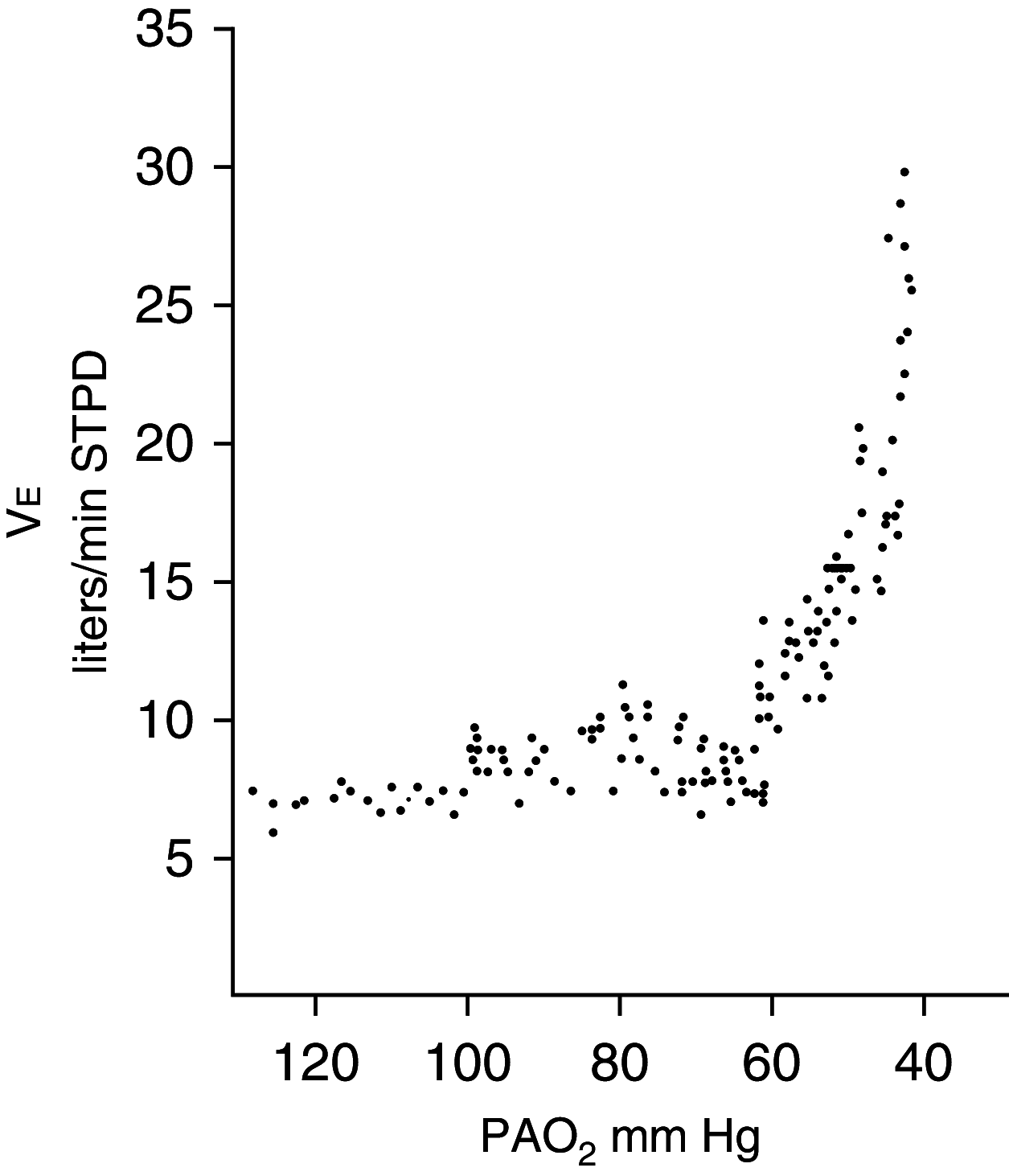
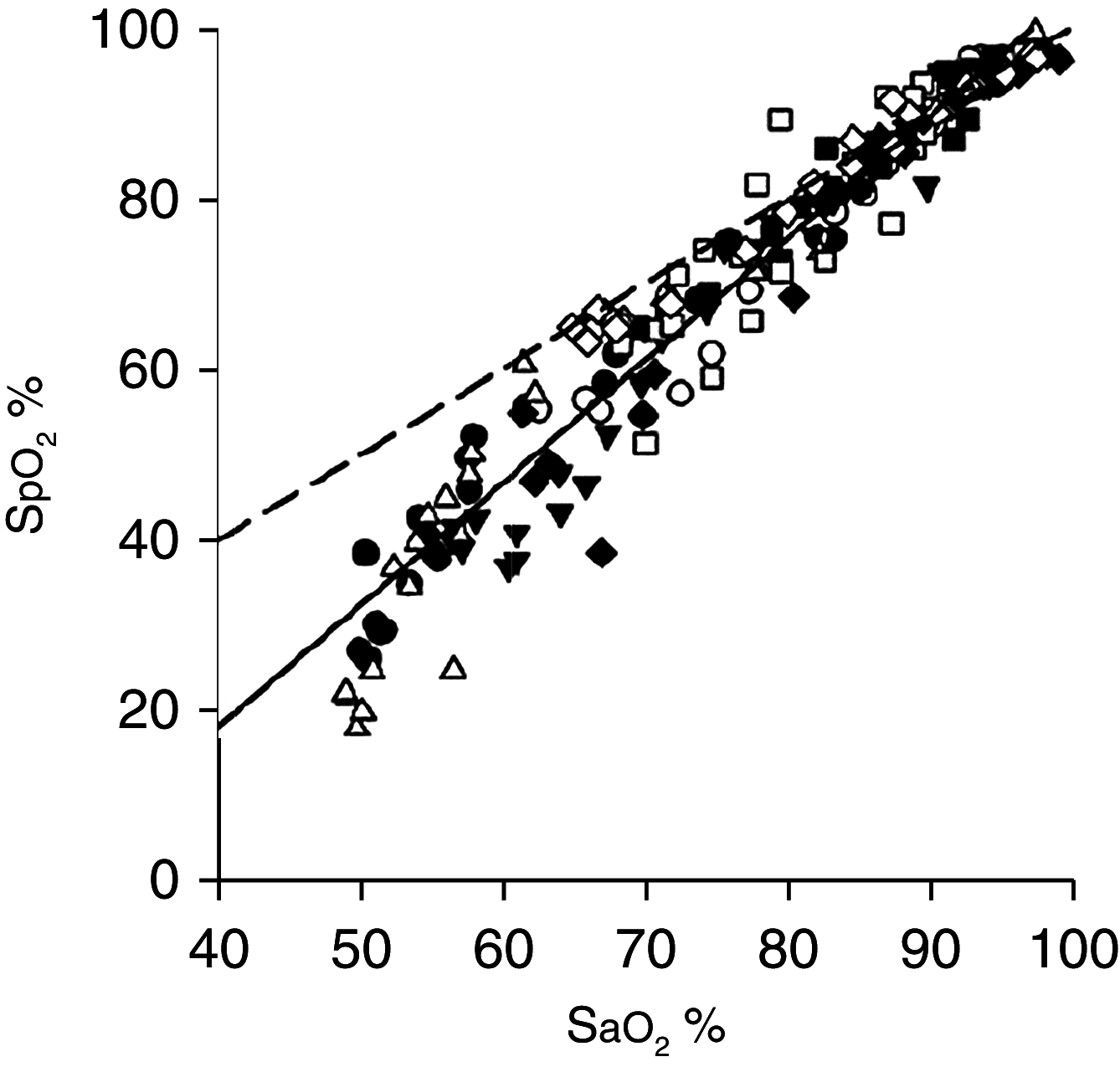
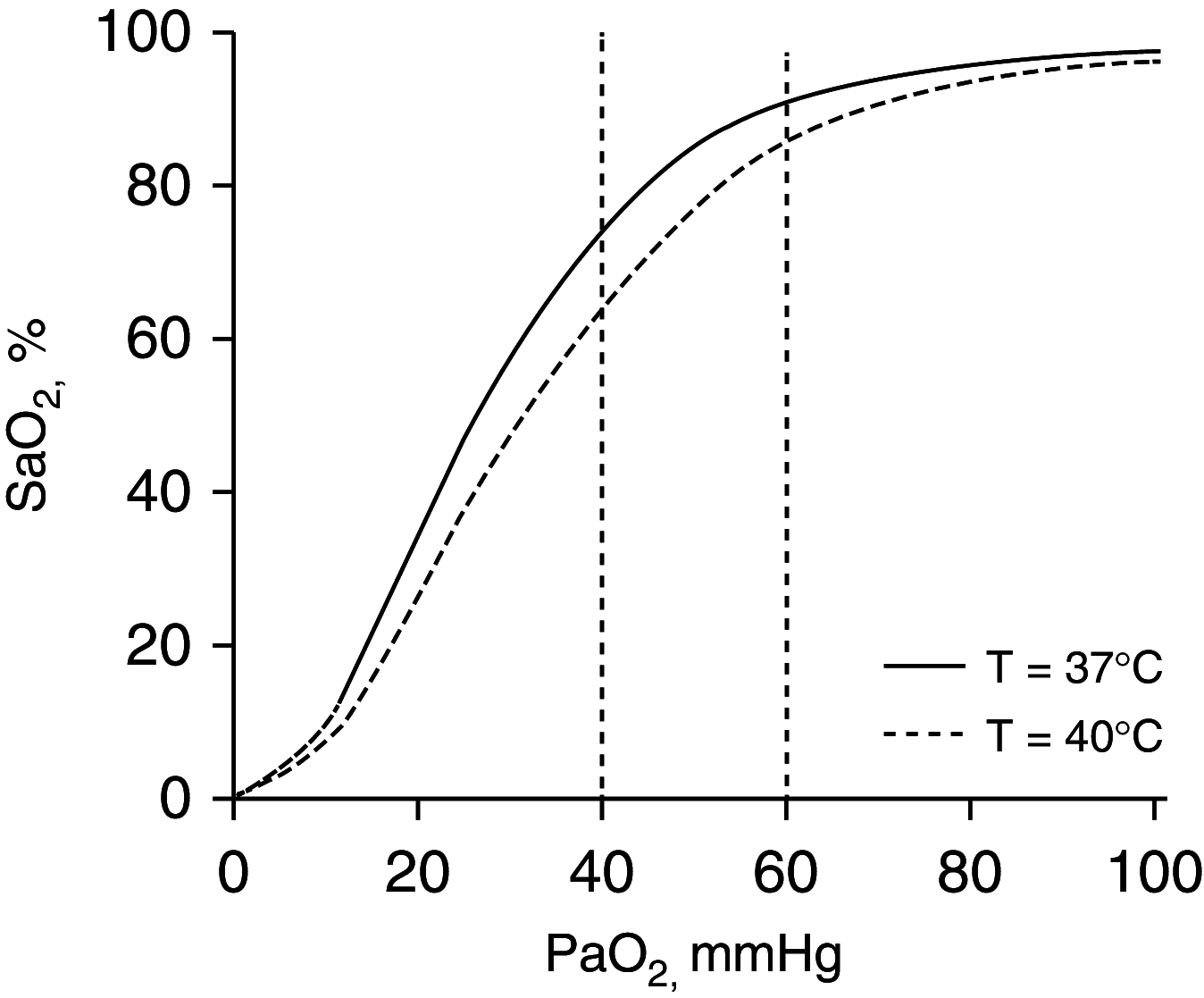
Patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) are described as exhibiting oxygen levels incompatible with life without dyspnea. The pairing-dubbed happy hypoxia but more precisely termed silent hypoxemia-is especially bewildering to physicians and is considered as defying basic biology. This combination has attracted extensive coverage in media but has not been discussed in medical journals. It is possible that coronavirus has an idiosyncratic action on receptors involved in chemosensitivity to oxygen, but well-established pathophysiological mechanisms can account for most, if not all, cases of silent hypoxemia. These mechanisms include the way dyspnea and the respiratory centers respond to low levels of oxygen, the way the prevailing carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) blunts the brain's response to hypoxia, effects of disease and age on control of breathing, inaccuracy of pulse oximetry at low oxygen saturations, and temperature-induced shifts in the oxygen dissociation curve. Without knowledge of these mechanisms, physicians caring for patients with hypoxemia free of dyspnea are operating in the dark, placing vulnerable patients with COVID-19 at considerable risk. In conclusion, features of COVID-19 that physicians find baffling become less strange when viewed in light of long-established principles of respiratory physiology; an understanding of these mechanisms will enhance patient care if the much-anticipated second wave emerges.
Keywords: COVID-19; control of breathing; dyspnea; hypoxemia; pulse oximetry.
Figures
Comment in
-
On Happy Hypoxia and on Sadly Ignored "Acute Vascular Distress Syndrome" in Patients with COVID-19.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Dec 1;202(11):1598-1599. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202006-2521LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32813543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Toy S, Roland D.Some doctors pull back on using ventilators to treat Covid-19 The Wall Street Journal 2020 May 11
-
- Couzin-Frankel J. The mystery of the pandemic’s ‘happy hypoxia’. Science. 2020;368:455–456. - PubMed
-
- Levitan R.The infection that’s silently killing coronavirus patients The New York Times 2020 Apr 20
-
- Preas HL, II, Jubran A, Vandivier RW, Reda D, Godin PJ, Banks SM, et al. Effect of endotoxin on ventilation and breath variability: role of cyclooxygenase pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:620–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

