Effectiveness of breathing exercises, foot reflexology and back massage (BRM) on labour pain, anxiety, duration, satisfaction, stress hormones and newborn outcomes among primigravidae during the first stage of labour in Saudi Arabia: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 32540887
- PMCID: PMC7299053
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033844
Effectiveness of breathing exercises, foot reflexology and back massage (BRM) on labour pain, anxiety, duration, satisfaction, stress hormones and newborn outcomes among primigravidae during the first stage of labour in Saudi Arabia: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
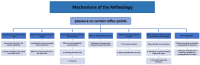
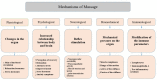
Introduction: Labour pain is among the severest pains primigravidae may experience during pregnancy. Failure to address labour pain and anxiety may lead to abnormal labour. Despite the many complementary non-pharmacological approaches to coping with labour pain, the quality of evidence is low and best approaches are not established. This study protocol describes a proposed investigation of the effects of a combination of breathing exercises, foot reflexology and back massage (BRM) on the labour experiences of primigravidae.
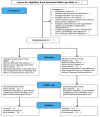
Methods and analysis: This randomised controlled trial will involve an intervention group receiving BRM and standard labour care, and a control group receiving only standard labour care. Primigravidae of 26-34 weeks of gestation without chronic diseases or pregnancy-related complications will be recruited from antenatal clinics. Eligible and consenting patients will be randomly allocated to the intervention or the control group stratified by intramuscular pethidine use. The BRM intervention will be delivered by a trained massage therapist. The primary outcomes of labour pain and anxiety will be measured during and after uterine contractions at baseline (cervical dilatation 6 cm) and post BRM hourly for 2 hours. The secondary outcomes include maternal stress hormone (adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol and oxytocin) levels, maternal vital signs (V/S), fetal heart rate, labour duration, Apgar scores and maternal satisfaction. The sample size is estimated based on the between-group difference of 0.6 in anxiety scores, 95% power and 5% α error, which yields a required sample size of 154 (77 in each group) accounting for a 20% attrition rate. The between-group and within-group outcome measures will be examined with mixed-effect regression models, time series analyses and paired t-test or equivalent non-parametric tests, respectively.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethical Committee for Research Involving Human Subjects of the Ministry of Health in the Saudi Arabia (H-02-K-076-0319-109) on 14 April 2019, and from the Ethics Committee for Research Involving Human Subjects (JKEUPM) Universiti Putra Malaysia on 23 October 2019, reference number: JKEUPM-2019-169. Written informed consent will be obtained from all participants. Results from this trial will be presented at regional, national and international conferences and published in indexed journals.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN87414969, registered 3 May 2019.
Keywords: breathing exercises; labour pain; massage; primigravidae; reflexology; stress hormones.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Breathing Exercises, Foot Reflexology and Massage (BRM) on Maternal and Newborn Outcomes Among Primigravidae in Saudi Arabia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Womens Health. 2022 Feb 25;14:279-295. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S347971. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35241937 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of foot reflexology massage on pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 10;14(1):1012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51107-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38200035 Free PMC article.
-
Does regular massage from late pregnancy to birth decrease maternal pain perception during labour and birth?--A feasibility study to investigate a programme of massage, controlled breathing and visualization, from 36 weeks of pregnancy until birth.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2006 Aug;12(3):222-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2005.12.006. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2006. PMID: 16835035
-
A pilot randomised controlled trial exploring the effects of antenatal reflexology on labour outcomes.Midwifery. 2017 Dec;55:137-144. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Midwifery. 2017. PMID: 29024881 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of breathing exercise on the duration of labour: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Glob Health. 2023 Mar 10;13:04023. doi: 10.7189/jogh.13.04023. J Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36896808 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-pharmacological labor pain relive methods: utilization and associated factors among midwives and maternity nurses in Najran, Saudi Arabia.Reprod Health. 2024 Jan 24;21(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12978-023-01737-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 38268021 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral recumbent position versus kneeling prone position combined with unprotected perineal delivery in natural childbirth: implication for clinical care.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Apr 3;25(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07497-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40181267 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Breathing Exercises, Foot Reflexology and Massage (BRM) on Maternal and Newborn Outcomes Among Primigravidae in Saudi Arabia: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Womens Health. 2022 Feb 25;14:279-295. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S347971. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35241937 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine therapy on labor pain in patients with natural childbirth: A network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e39425. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039425. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470555 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of foot reflexology massage on pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 10;14(1):1012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-51107-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38200035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devilata T, Swarna S. Effectiveness of pre delivery preparation on anxiety among primigravida mothers at maternal child health centre Tirupati, AP, India. IOSR J Nurs Heal Sci 2015;4:19–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
