Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability
- PMID: 32540902
- PMCID: PMC7299281
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abc5902
Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability
Abstract
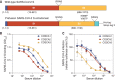
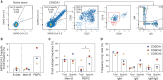
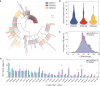
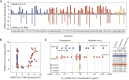
The rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has had a large impact on global health, travel, and economy. Therefore, preventative and therapeutic measures are urgently needed. Here, we isolated monoclonal antibodies from three convalescent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients using a SARS-CoV-2 stabilized prefusion spike protein. These antibodies had low levels of somatic hypermutation and showed a strong enrichment in VH1-69, VH3-30-3, and VH1-24 gene usage. A subset of the antibodies was able to potently inhibit authentic SARS-CoV-2 infection at a concentration as low as 0.007 micrograms per milliliter. Competition and electron microscopy studies illustrate that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein contains multiple distinct antigenic sites, including several receptor-binding domain (RBD) epitopes as well as non-RBD epitopes. In addition to providing guidance for vaccine design, the antibodies described here are promising candidates for COVID-19 treatment and prevention.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
References
-
- Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X., Qu J., Gong F., Han Y., Qiu Y., Wang J., Liu Y., Wei Y., Xia J., Yu T., Zhang X., Zhang L., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 395, 507–513 (2020). 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mair-Jenkins J., Saavedra-Campos M., Baillie J. K., Cleary P., Khaw F.-M., Lim W. S., Makki S., Rooney K. D., Nguyen-Van-Tam J. S., Beck C. R.; Convalescent Plasma Study Group , The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 211, 80–90 (2015). 10.1093/infdis/jiu396 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ko J. H., Seok H., Cho S. Y., Ha Y. E., Baek J. Y., Kim S. H., Kim Y. J., Park J. K., Chung C. R., Kang E.-S., Cho D., Müller M. A., Drosten C., Kang C.-I., Chung D. R., Song J.-H., Peck K. R., Challenges of convalescent plasma infusion therapy in Middle East respiratory coronavirus infection: A single centre experience. Antivir. Ther. 23, 617–622 (2018). 10.3851/IMP3243 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shen C., Wang Z., Zhao F., Yang Y., Li J., Yuan J., Wang F., Li D., Yang M., Xing L., Wei J., Xiao H., Yang Y., Qu J., Qing L., Chen L., Xu Z., Peng L., Li Y., Zheng H., Chen F., Huang K., Jiang Y., Liu D., Zhang Z., Liu Y., Liu L., Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA 323, 1582 (2020). 10.1001/jama.2020.4783 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

