Alterations in Enteroendocrine Hormones After Total Pancreatectomy With Islet Autotransplantation
- PMID: 32541637
- PMCID: PMC7321866
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001582
Alterations in Enteroendocrine Hormones After Total Pancreatectomy With Islet Autotransplantation
Abstract
Objective: When total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation (TPIAT) is performed for chronic pancreatitis, the pancreas and most of the duodenum are removed, with Roux-en-Y reconstruction of the gastrointestinal tract. Enteroendocrine cells in the intestines and pancreas secrete hormones coordinating digestion and motility, but anatomic reconstruction alters transit of nutrients to these cells. We hypothesized that TPIAT leads to changes in enteroendocrine hormones.
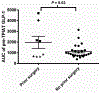
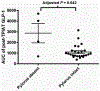
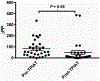
Methods: Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), peptide YY (PYY), and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) were measured from mixed-meal tolerance tests of 34 clinical trial participants before and 18 months after TPIAT. Area under the curve of GLP-1 and PYY-stimulated responses were calculated by trapezoidal method, and the PP response was measured as the stimulated max minus baseline (ΔPP).
Results: Area under the curve of GLP-1 and PYY increased significantly after TPIAT (GLP-1 average +553.1 pg/mL per minute, P = 0.004; PYY average +4647.9 pg/mL per minute, P = 0.02). ΔPP trended toward lower after TPIAT (average, -52.2 pg/mL, P = 0.06).
Conclusions: In this novel study of enteroendocrine hormones in TPIAT patients, stimulated levels of GLP-1 and PYY were significantly higher after versus before TPIAT. ΔPP was lower after TPIAT, but not significantly. These hormone changes have potential clinical implications that warrant further research.
Figures

References
-
- Pant C, Sferra TJ. Emergency Department Visits and Hospitalizations in Children With Chronic Pancreatitis in the United States. J Pediatr Gastroenterol and Nutr. 2015;61:568–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

