Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell-restricted Cdx2 expression induces transformation to myelodysplasia and acute leukemia
- PMID: 32541670
- PMCID: PMC7296000
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16840-2
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell-restricted Cdx2 expression induces transformation to myelodysplasia and acute leukemia
Abstract
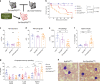
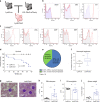
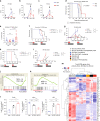
The caudal-related homeobox transcription factor CDX2 is expressed in leukemic cells but not during normal blood formation. Retroviral overexpression of Cdx2 induces AML in mice, however the developmental stage at which CDX2 exerts its effect is unknown. We developed a conditionally inducible Cdx2 mouse model to determine the effects of in vivo, inducible Cdx2 expression in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Cdx2-transgenic mice develop myelodysplastic syndrome with progression to acute leukemia associated with acquisition of additional driver mutations. Cdx2-expressing HSPCs demonstrate enrichment of hematopoietic-specific enhancers associated with pro-differentiation transcription factors. Furthermore, treatment of Cdx2 AML with azacitidine decreases leukemic burden. Extended scheduling of low-dose azacitidine shows greater efficacy in comparison to intermittent higher-dose azacitidine, linked to more specific epigenetic modulation. Conditional Cdx2 expression in HSPCs is an inducible model of de novo leukemic transformation and can be used to optimize treatment in high-risk AML.
Conflict of interest statement
We have the following disclosures that have been included in the manuscript as potential for conflict of interest. This work was funded by the National Health and Medical Research Fund of Australia and the Leukaemia Foundation of Australia. Celgene provided azacitidine and additional research funding. S.W.L. has participated in an advisory board for Celgene.
Figures




References
-
- Rawat VPS, et al. Overexpression of Cdx2 perturbs Hox gene expression in murine progenitors depending on its N-Terminal domain and is closely correlated with deregulated Hox gene expression in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2007;111:309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

