A Neuroprotective Dose of Isatin Causes Multilevel Changes Involving the Brain Proteome: Prospects for Further Research
- PMID: 32545384
- PMCID: PMC7313464
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21114187
A Neuroprotective Dose of Isatin Causes Multilevel Changes Involving the Brain Proteome: Prospects for Further Research
Abstract
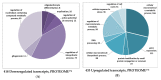
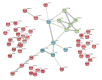
Isatin (indole-2,3-dione) is an endogenous regulator, exhibiting a wide range of biological and pharmacological activities. At doses of 100 mg/kg and above, isatin is neuroprotective in different experimental models of neurodegeneration. Good evidence exists that its effects are realized via interaction with numerous isatin-binding proteins identified in the brain and peripheral tissues studied. In this study, we investigated the effect of a single dose administration of isatin to mice (100 mg/kg, 24 h) on differentially expressed proteins and a profile of the isatin-binding proteins in brain hemispheres. Isatin administration to mice caused downregulation of 31 proteins. However, these changes cannot be attributed to altered expression of corresponding genes. Although at this time point isatin influenced the expression of more than 850 genes in brain hemispheres (including 433 upregulated and 418 downregulated genes), none of them could account for the changes in the differentially expressed proteins. Comparative proteomic analysis of brain isatin-binding proteins of control and isatin-treated mice revealed representative groups of proteins sensitive to isatin administration. Control-specific proteins (n = 55) represent specific targets that interact directly with isatin. Appearance of brain isatin-binding proteins specific to isatin-treated mice (n = 94) may be attributed to the formation of new clusters of protein-protein interactions and/or novel binding sites induced by a high concentration of this regulator (ligand-induced binding sites). Thus, isatin administration produces multiple effects in the brain, which include changes in gene expression and also profiles of isatin-binding proteins and their interactomes. Further studies are needed for deeper insight into the mechanisms of the multilevel changes in the brain proteome induced by isatin. In the context of the neuroprotective action, these changes may be aimed at interruption of pathological links that begin to form after initiation of pathological processes.
Keywords: differentially expressed proteins; interactome; isatin-binding proteins; molecular targets; neuroprotector isatin; proteome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tryptophan Metabolites as Mediators of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Communication: Focus on Isatin.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:922274. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.922274. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35846785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The effect of deprenyl and isatin administration to mice on the proteomic profile of liver isatin-binding proteins].Biomed Khim. 2018 Aug;64(4):354-359. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20186404354. Biomed Khim. 2018. PMID: 30135283 Russian.
-
[The effect of a neuroprotective dose of isatin or deprenyl to mice on the profile of brain isatin-binding proteins].Biomed Khim. 2019 Aug;65(5):407-417. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20196505407. Biomed Khim. 2019. PMID: 31666414 Russian.
-
[The effect of neurotoxin MPTP administration to mice on the proteomic profile of brain isatin-binding proteins].Biomed Khim. 2017 Jul;63(4):316-320. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20176304316. Biomed Khim. 2017. PMID: 28862602 Russian.
-
Isatin, an endogenous nonpeptide biofactor: A review of its molecular targets, mechanisms of actions, and their biomedical implications.Biofactors. 2018 Mar;44(2):95-108. doi: 10.1002/biof.1408. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Biofactors. 2018. PMID: 29336068 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorus-Derived Isatin Hydrazones: Synthesis, Structure, Thromboelastography, Antiplatelet, and Anticoagulation Activity Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;26(13):6147. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136147. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649924 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical Ubiquitination and Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;23(7):3705. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073705. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tryptophan Metabolites as Mediators of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Communication: Focus on Isatin.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 30;16:922274. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.922274. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35846785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of CIAPIN1 (Cytokine-Induced Apoptosis Inhibitor 1) Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 1;11(13):3826. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133826. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35807116 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the Affinity-Enhancing Effect of Isatin on Human Ferrochelatase and Adrenodoxin Reductase Complex Formation: Implication for Protein Interactome Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 14;21(20):7605. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207605. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33066693 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

