COVID-19 Infection Diagnosis: Potential Impact of Isothermal Amplification Technology to Reduce Community Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32545412
- PMCID: PMC7345291
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10060399
COVID-19 Infection Diagnosis: Potential Impact of Isothermal Amplification Technology to Reduce Community Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
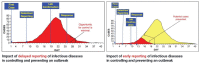
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is largely driven by community transmission, after 2019 novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV or SARS-CoV-2) crosses the borders. To stop the spread, rapid testing is required at community clinics and hospitals. These rapid tests should be comparable with the standard PCR technology. Isothermal amplification technology provides an excellent alternative that is highly amenable to resource limited settings, where expertise and infrastructure to support PCR are not available. In this review, we provide a brief description of isothermal amplification technology, its potential and the gaps that need to be considered for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Among this emerging technology, loop-mediated amplification (LAMP), recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and Nicking enzyme-assisted reaction (NEAR) technologies have been identified as potential platforms that could be implemented at community level, without samples referral to a centralized laboratory and prolonged turnaround time associated with the standard COVID-19 RT-PCR test. LAMP, for example, has recently been shown to be comparable with PCR and could be performed in less than 30 min by non-laboratory staff, without RNA extractions commonly associated with PCR. Interestingly, NEAR (ID NOW™ COVID-19 (Abbott, IL, USA) was able to detect the virus in 5 min. More so, isothermal platforms are cost effective and could easily be scaled up to resource limited settings. Diagnostics developers, scientific community and commercial companies could consider this alternative method to help stop the spread of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; LAMP, RPA, NEAR; novel coronavirus; point of care testing; rapid testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Situation Report 11. [(accessed on 13 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/defaultsource/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20....
-
- Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Situation Report 48. [(accessed on 13 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/defaultsource/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20....
-
- The Global Coronavirus Recession Is Beginning. [(accessed on 13 March 2020)]; Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2020/03/16/economy/global-recession-coronavirus/....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

