Impact of the Burden of COVID-19 in Italy: Results of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) and Productivity Loss
- PMID: 32545827
- PMCID: PMC7345321
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17124233
Impact of the Burden of COVID-19 in Italy: Results of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) and Productivity Loss
Abstract
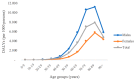
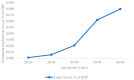
The WHO declared the novel coronavirus disease a pandemic, with severe consequences for health and global economic activity and Italy is one of the hardest hit countries. This study aims to assess the socio-economic burden of COVID-19 pandemic in Italy through the estimation of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) and productivity loss. The observational study was based on data from official governmental sources collected since the inception of epidemic until 28 April 2020. DALYs for a disease combines the years of life lost due to premature mortality in the population and the years lost due to disability of the disease. In addition to DALYs, temporary productivity loss due to absenteeism from work and permanent productivity loss due to premature mortality were estimated using the Human Capital Approach. The total DALYs amount to 2.01 per 1000 persons. The total permanent productivity loss was around EUR 300 million while the temporary productivity loss was around EUR 100 million. This evaluation does not consider other economic aspects related to lockdown, quarantine of contacts, healthcare direct costs etc. The burden of disease methodology is functional metric for steering choices of health policy and allowing the government to be accountable for the utilization of resources.
Keywords: COVID-19; DALY; YLD; YLL; coronavirus; pandemic; productivity loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ministero Della Salute FAQ—Covid-19. [(accessed on 4 May 2020)]; Available online: http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/malattieInfettive/dettaglioFaqMalattieI....
-
- Mayo Clinic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [(accessed on 4 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/symptoms-caus....
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report—51. [(accessed on 4 May 2020)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) JHU (JHU) COVID-19 Dashboard. [(accessed on 5 May 2020)]; Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità ISS per COVID-19. [(accessed on 5 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.iss.it/en/coronavirus.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous