The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of Reed Canary Grass (Phalaris arundinacea) and Hardinggrass (P. aquatica)
- PMID: 32545897
- PMCID: PMC7356517
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9060748
The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of Reed Canary Grass (Phalaris arundinacea) and Hardinggrass (P. aquatica)
Abstract
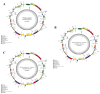
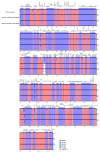
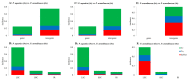
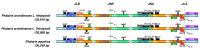
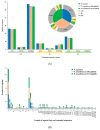
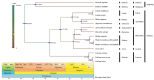
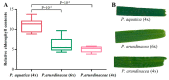
There are 22 species in the Phalaris genera that distribute almost all over the temperate regions of the world. Among them, reed canary grass (Phalaris arundinacea, tetraploid and hexaploid) and hardinggrass (P. aquatica, tetraploid) have been long cultivated as forage grass and have received attention as bio-energy materials in recent years. We aimed to facilitate inter-species/ploidies comparisons, and to illuminate the degree of sequence variation within existing gene pools, chloroplast (cp) genomes of three Phalaris cytotypes (P. aquatica/4x, P. arundinacea/4x and P. arundinacea/6x) were sequenced and assembled. The result indicated that certain sequence variations existed between the cp genomes of P. arundinacea and P. aquatica. Several hotspot regions (atpI~atpH, trnT-UGU~ndhJ, rbcL~psaI, and ndhF~rpl32) were found, and variable genes (infA, psaI, psbK, etc.) were detected. SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) and/or indels (insertions and deletions) were confirmed by the high Ka/Ks and Pi value. Furthermore, distribution and presence of cp simple sequence repeats (cpSSRs) were identified in the three Phalaris cp genomes, although little difference was found between hexaploid and tetraploid P. arundinacea, and no rearrangement was detected among the three Phalaris cp genomes. The evolutionary relationship and divergent time among these species were discussed. The RNA-seq revealed several differentially expressed genes (DEGs), among which psaA, psaB, and psbB related to leaf color were further verified by leaf color differences.
Keywords: Phalaris aquatica L.; Phalaris arundinacea L.; RNA-seq; chloroplast genome; high-throughput sequencing; ploidy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ravi V., Khurana J.P., Tyagi A.K., Khurana P. An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant Syst. Evol. 2008;271:101–122. doi: 10.1007/s00606-007-0608-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

