Increased risk of tinnitus in patients with early-onset cataracts: a nationwide population-based case-control study
- PMID: 32546219
- PMCID: PMC7298820
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-020-01497-8
Increased risk of tinnitus in patients with early-onset cataracts: a nationwide population-based case-control study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the association between early-onset cataract and tinnitus using a population-based database.
Methods: Retrospective claims data from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database were analysed. Study subjects comprised patients with early-onset cataract, aged 20-55 years and diagnosed between 2000 and 2010 (n = 2084) and a comparison cohort without the disease (n = 8336). Both cohorts were followed until 2010 to estimate the incidence of tinnitus. To calculate the risk of tinnitus in the case and control groups, Cox proportional hazards models were used and presented as hazard ratios (HRs), adjusted HRs (aHRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
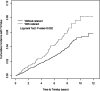
Results: Patients with early-onset cataract had 1.53-fold increased risk (HR = 1.53, 95% CI = 1.17-2.01, p < 0.01) of developing tinnitus than controls. The number of patients with vertigo (p < 0.0001), insomnia (p < 0.0001), anxiety (p < 0.0001) and hearing loss (p < 0.0001) as comorbidities was also significantly higher in the case group. After adjusting for age, sex and all listed comorbidities, patients with increasing age (aHR = 1.04, 95% CI = 1.02-1.07), early-onset cataract (aHR = 1.32, 95% CI = 1.01-1.74), vertigo (aHR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.15-2.67), insomnia (aHR = 1.48, 95% CI = 1.14-1.93) and hearing loss (aHR = 6.20, 95% CI = 3.58-10.70) had significantly higher risk of tinnitus.
Conclusions: Patients with early-onset cataract are at an increased risk of developing tinnitus in subsequent years and should receive further evaluation for early diagnosis and management if any signs of tinnitus occur.
Keywords: Case-control; Cohort study; Early-onset cataract; Risk; Tinnitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Incidence of Tinnitus Following a Hyperthyroidism Diagnosis: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 3;12:741719. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.741719. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34803911 Free PMC article.
-
Increased risk of cancer in patients with early-onset cataracts: a nationwide population-based study.Cancer Sci. 2014 Apr;105(4):431-6. doi: 10.1111/cas.12360. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24450445 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothyroidism and related comorbidities on the risks of developing tinnitus.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 1;12(1):3401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07457-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35233053 Free PMC article.
-
Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with increased risk of insomnia: a nationwide population-based cohort study.J Clin Sleep Med. 2022 May 1;18(5):1335-1342. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.9864. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 34978279 Free PMC article.
-
Increased risk of peptic ulcer in patients with early-onset cataracts: A nationwide population-based study.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 9;13(11):e0207193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207193. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30412615 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tinnitus: Clinical Insights in Its Pathophysiology-A Perspective.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2024 Jun;25(3):249-258. doi: 10.1007/s10162-024-00939-0. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38532055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factor Analysis of Early-Onset Cataracts in Taiwan.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 23;11(9):2374. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092374. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Priority Eye Disease 2. Cataract. https://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index1.htm.
-
- Joe A. Vinson. Oxidative stress in cataracts. Pathophysiology. 2006;13(3):151–162. - PubMed
-
- Truscott RJ. Age-related nuclear cataract-oxidation is the key. Exp Eye Res. 2005;80:709–725. - PubMed
-
- Tsai SY, Hsu WM, Cheng CY, Liu JH, Chou P. Epidemiologic study of age-related cataracts among an elderly Chinese population in Shih-Pai Taiwan. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1089–1095. - PubMed
-
- Prchal J, Skalka H, Clements RS, Bradley EL, Conrad ME, Pittman C. Diabetes and risk of cataract development. Metab Pediatr Ophthalmol. 1980;4:185–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical