Validity and Reliability of the Flourishing Scale in a Sample of Older Adults in Iran
- PMID: 32546985
- PMCID: PMC7244746
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S251067
Validity and Reliability of the Flourishing Scale in a Sample of Older Adults in Iran
Abstract
Background: Flourishing is related to positive outcomes for physical and mental health, as well as overall wellbeing. The aim of the present study was to determine the validity and reliability of the Flourishing Scale (FS) among a sample of older participants in Iran.
Methods: In this validation study, 300 older people were selected by cluster sampling method. Data were collected using a checklist for demographic characteristics, the FS, and the Oxford happiness questionnaire. The validity (face, content, convergent, and construct) and reliability (Cronbach's alpha, test-retest) of the FS was evaluated in this cross-sectional study.
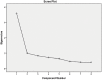
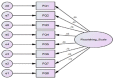
Results: The exploratory factor analysis demonstrated a one-dimensional structure consisting of 8 items with an eigenvalue of 3.583. The model had a good fit [χ2 = 52.983, p < 0.001, χ2/df = 2.944, GFI = 0.958, CFI = 0.915, IFI = 0.949, TLI = 0.919, AGFI = 0.948, and RMSEA = 0.081, SRMR = 0.086] with all factor loadings greater than 0.5 and statistically significant. A test of concurrent validity showed a direct and significant association between the FS and the Oxford happiness questionnaire (r = 0.647, p < 0.001). The results of the reliability tests confirmed that the values of Cronbach's alpha coefficient (0.819) and test-retest (0.821) were acceptable.
Conclusion: The Persian version of the FS demonstrated suitable validity and reliability among a sample of older participants.
Keywords: aging; factor analysis; flourishing; reliability; validity.
© 2020 Fassih-Ramandi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comments on "Validity and Reliability of the Flourishing Scale in a Sample of Older Adults in Iran" [Letter].Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Jul 9;15:1097-1098. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S268539. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 32764896 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bahrami N, Moradi M, Soleimani M, Kalantari Z, Hosseini F. Death anxiety and its relationship with quality of life in women with cancer. Iran J Nurs. 2013;26(82):51–61.
-
- Aliakbari Dehkordi M, Peymanfar E, Mohtashami T, Borjali A. The comparison of different levels of religious attitude on sense of meaning, loneliness and happiness in life of elderly persons under cover of social welfare organisation of urmia City. Salmand. 2015;9(4):297–305.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous