Conventional and Nanotechnology Based Approaches to Combat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Implications for Chronic Airway Diseases
- PMID: 32547029
- PMCID: PMC7266405
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S242516
Conventional and Nanotechnology Based Approaches to Combat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Implications for Chronic Airway Diseases
Abstract
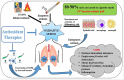
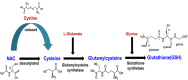
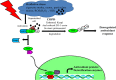
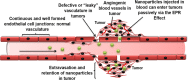
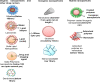
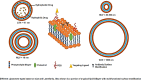
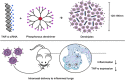
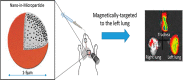
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the most prevalent obstructive lung disease worldwide characterized by decline in lung function. It is associated with airway obstruction, oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and enhanced autophagy and cellular senescence. Cigarette smoke being the major risk factor, other secondary risk factors such as the exposure to air pollutants, occupational exposure to gases and fumes in developing countries, also contribute to the pathogenesis of COPD. Conventional therapeutic strategies of COPD are based on anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory drugs. However, traditional anti-oxidant pharmacological therapies are commonly used to alleviate the impact of COPD as they have many associated repercussions such as low diffusion rate and inappropriate drug pharmacokinetics. Recent advances in nanotechnology and stem cell research have shed new light on the current treatment of chronic airway disease. This review is focused on some of the anti-oxidant therapies currently used in the treatment and management of COPD with more emphasis on the recent advances in nanotechnology-based therapeutics including stem cell and gene therapy approaches for the treatment of chronic airway disease such as COPD and asthma.
Keywords: COPD; anti-oxidant therapy; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; gene therapy; nanotechnology; stem cell therapy.
© 2020 Passi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nano-based theranostics for chronic obstructive lung diseases: challenges and therapeutic potential.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011 Sep;8(9):1105-9. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2011.597381. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011. PMID: 21711085 Free PMC article.
-
Biological effects and mechanisms of action of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Int Med Res. 2015 Jun;43(3):303-10. doi: 10.1177/0300060514568733. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Int Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25834280 Review.
-
Novel drug delivery systems targeting oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Oct 19;18(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00703-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 33076918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidants in asthma and in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(16):2053-62. doi: 10.2174/1381612054065774. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 15974958 Review.
-
Hydrogen-rich saline inhibits tobacco smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by alleviating airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in rats.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Sep;242(15):1534-1541. doi: 10.1177/1535370217725249. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28795606 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular dynamics simulation insights into the cellular uptake of elastic nanoparticles through human pulmonary surfactant.RSC Adv. 2022 Aug 25;12(37):24222-24231. doi: 10.1039/d2ra03670c. eCollection 2022 Aug 22. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36128539 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Inhalation Therapy for Pulmonary Diseases.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(11):882-896. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220803103039. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35927812
-
Current views in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis and management.Saudi Pharm J. 2021 Dec;29(12):1361-1373. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.10.008. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Saudi Pharm J. 2021. PMID: 35002373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic Liposomes with Different Lipid Ratios: Antibacterial Activity, Antibacterial Mechanism, and Cytotoxicity Evaluations.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;15(12):1556. doi: 10.3390/ph15121556. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559007 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Based Nanocarriers for Pulmonary and Intranasal Drug Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Overview of their Applications.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(7):492-511. doi: 10.2174/0113894501301747240417103321. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38676513 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

