Factors Related to Severity of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32547145
- PMCID: PMC7259447
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S256243
Factors Related to Severity of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is one of the diabetes complications. DFU can be the cause of a high rate of amputation, health-care costs and even death, and this condition occurs in the severity status of DFU. Severity of DFU is the cause of expensive complication incidence. Understanding the factors affecting it can help preventive functions. Adequate evidence for this problem is necessary. The aim of this systematic review is to summarize evidence on severity of diabetic foot ulcer.
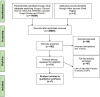
Methods: A literature search was undertaken in Scopus, PubMed, Elsevier, MEDLINE, Embase, UpToDate and Google Scholar. Observational studies that assessed severity of DFU were included. The data extraction and assessment are on the basis of PRISMA.
Results: Seven studies were assessed and 25 factors that affect severity of DFU are reported in the studies. The most used score for an estimate of severity was the Wagner scale (n=5). The majority of patients were in G1 and G2 stages (67.5%; basis of Wagner) or have a superficial ulcer (62.84%) on the basis of the Texas Diabetic Wound Classification System. The main factors include high BMI, smoking, lack of diabetes control, type of diabetes treatment and older age. In addition, there were other factors that affect severity of DFU such as vascular complications, bacteria isolated, marital status, gender, high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. Also, life location, type 2 diabetes, genotype, addiction, long-time DFU and delay to refer patients were other factors.
Conclusion: Twenty-five factors were reported. The majority of these factors related to life-style and can be prevented by self-care functions. The effect of these factors needs further study and the further studies must be better in quality.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic foot ulcer; severity.
© 2020 Jalilian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th edition; 2019. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/en/. Accessed December13, 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources