Phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate: A novel actor in thrombopoiesis and thrombosis
- PMID: 32548550
- PMCID: PMC7292656
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12321
Phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate: A novel actor in thrombopoiesis and thrombosis
Abstract
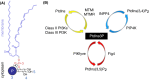
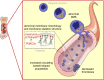
Phosphoinositides are lipid second messengers regulating in time and place the formation of protein complexes involved in the control of intracellular signaling, vesicular trafficking, and cytoskeleton/membrane dynamics. One of these lipids, phosphatidylinositol 3 monophosphate (PtdIns3P), is present in small amounts in mammalian cells and is involved in the control of endocytic/endosomal trafficking and in autophagy. Its metabolism is finely regulated by specific kinases and phosphatases including class II phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3KC2s) and the class III PI3K, Vps34. Recently, PtdIns3P has emerged as an important regulator of megakaryocyte/platelet structure and functions. Here, we summarize the current knowledge in the role of different pools of PtdIns3P regulated by class II and III PI3Ks in platelet production and thrombosis. Potential new antithrombotic therapeutic perspectives based on the use of inhibitors targeting specifically PtdIns3P-metabolizing enzymes will also be discussed. Finally, we provide report of new research in this area presented at the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2019 Annual Congress.
Keywords: megakaryocytes; phosphatidylinositol 3 monophosphate; phosphoinositide 3‐kinases; platelets; thrombosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Viaud J, Mansour R, Antkowiak A, Mujalli A, Valet C, Chicanne G, et al. Phosphoinositides: important lipids in the coordination of cell dynamics. Biochimie. 2016;125:250–8. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki T, Takasuga S, Sasaki J, Kofuji S, Eguchi S, Yamazaki M, et al. Mammalian phosphoinositide kinases and phosphatases. Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48(6):307–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

