Linac-based fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with a micro-multileaf collimator for large brain metastasis unsuitable for surgical resection
- PMID: 32548618
- PMCID: PMC7336818
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rraa038
Linac-based fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with a micro-multileaf collimator for large brain metastasis unsuitable for surgical resection
Abstract
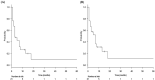
The aim of this study was to assess clinical outcomes using linac-based, fractionated, stereotactic radiotherapy (fSRT) with a micro-multileaf collimator for large brain metastasis (LBM) unsuitable for surgical resection. Between January 2009 and October 2018 we treated 21 patients with LBM using linac-based fSRT. LBM was defined as a tumor with ≥30 mm maximal diameter in gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance images. LBMs originated from the lung (n = 17, 81%), ovary (n = 2, 9.5%), rectum (n = 1, 4.8%) and esophagus (n = 1, 4.8%). The median pretreatment Karnofsky performance status was 50 (range: 50-80). Recursive partition analysis (RPA) was as follows: Classes 2 and 3 were 7 and 14 patients, respectively. The median follow-up was 5 months (range: 1-86 months). The range of tumor volume was 8.7-26.5 cm3 (median: 17.1 cm3). All patients were basically treated with 35Gy in 5 fractions, except in three cases. The progression-free survival was 3.0 months. The median survival time was 7.0 months. There was no permanent radiation injury in any of the patients. Radiation-caused central nervous system necrosis, according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0, occurred in one patient (grade 3). One patients received bevacizumab for radiation necrosis. Two patients underwent additional surgical resection due to local progression and cyst formation. For patients with LBM unsuitable for surgical resection, linac-based fSRT is a promising therapeutic alternative.
Keywords: Novalis; fractionated radiotherapy; large brain metastasis; stereotactic radiotherapy.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with a micro-multileaf collimator for brain metastasis in the primary motor cortex.J Radiat Res. 2022 Jan 20;63(1):63-70. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab111. J Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 34927204 Free PMC article.
-
Linac-Based Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy with a Micro-Multileaf Collimator for Brainstem Metastasis.World Neurosurg. 2019 Dec;132:e680-e686. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.049. Epub 2019 Aug 21. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31442651
-
Clinical Results and Hematologic Predictors of Linear Accelerator-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery or Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastasis in Patients Aged 75 Years or Older: A Retrospective Study.World Neurosurg. 2024 Mar;183:e944-e952. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.01.069. Epub 2024 Jan 19. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38244685
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of intracranial meningiomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Jun 1;46(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1970. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 31153149
-
[Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy for brain metastases].Bull Cancer. 2013 Jan 1;100(1):75-81. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2012.1683. Bull Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23376580 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Salvage Surgical Resection after Linac-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Newly Diagnosed Brain Metastasis.Curr Oncol. 2021 Dec 9;28(6):5255-5265. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28060439. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34940078 Free PMC article.
-
Linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with a micro-multileaf collimator for brain metastasis in the primary motor cortex.J Radiat Res. 2022 Jan 20;63(1):63-70. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab111. J Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 34927204 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Survival after Linac-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy with a Micro-Multileaf Collimator for Brain Metastasis.Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 24;29(9):6068-6076. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090477. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135046 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammation response index predicts overall survival in patients undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer.J Radiat Res. 2025 Mar 24;66(2):129-136. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae099. J Radiat Res. 2025. PMID: 39967449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolf A, Kvint S, Chachoua A et al. . Toward the complete control of brain metastases using surveillance screening and stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 2018;128:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson SD, Wagner KM, Prabhu SS et al. . Neurosurgical management of brain metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 2017;34:377–89. - PubMed
-
- Lee CC, Yen CP, Xu Z et al. . Large intracranial metastatic tumors treated by gamma knife surgery: Outcomes and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg 2014;120:52–9. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa T, Kato T, Yamamoto T et al. . Multisession gamma knife surgery for large brain metastases. J Neurooncol 2017;131:517–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical