Effect of a bundle of intervention strategies for the control of COVID-19 in Henan, a neighboring province of Wuhan, China
- PMID: 32548764
- PMCID: PMC7296893
- DOI: 10.1007/s00508-020-01688-9
Effect of a bundle of intervention strategies for the control of COVID-19 in Henan, a neighboring province of Wuhan, China
Abstract
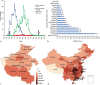
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) occurred in China (mainly in Wuhan, Hubei Province) at the end of December 2019. Henan province is located in the center of China, borders on Hubei province by land in the south with the nearest distance of 200 kilometers to Wuhan. As the inland provinces in mainland China, frequent communication in transportation and population flow make it difficult to confine the pandemic, which is similar to that in the landlocked countries in Europe. The expected cases in Henan were mainly imported. A bundle of intervention strategies were adopted from 26 January 2020 to cut off the spread between the infected patients and the native residents. The pandemic was controlled 2 month later after the bundle of strategies was adopted although the number of cases continued to increase explosively during the first 10 days. A total of 1273 cases were confirmed, 1251 patients were cured, 22 patients died, and 1 patient was still in hospital until 29 March 2020. The peak of daily increased cases was 109 cases. Our data show that COVID-19 is highly infectious and easy to cause an outbreak, but it can be controlled by early effective interventions. A bundle of strategies according to the specific situation of each country is suggested to be implemented as early as possible.
Keywords: Control strategy; Corona virus; Droplet transmission; Mask; Pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
Q. Liu, H. Lu, and R. Chen declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- CDC of China. Distribution of novel coronavirus pneumonia. 2020. http://2019ncov.chinacdc.cn/2019-nCoV/. Accessed 29 March 2020
-
- Henan.gov. Announcement on prevention and control of novel coronavirus pneumonia. 2020. https://www.henan.gov.cn/2020/01-26/1285120.html. Accessed 29 March 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

