Varietal classification of white wines by fluorescence spectroscopy
- PMID: 32549605
- PMCID: PMC7271340
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04291-y
Varietal classification of white wines by fluorescence spectroscopy
Abstract
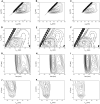
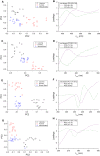
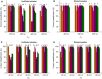
The Slovak Tokaj region is one of the producers of high-quality white wine having protected designations of origin. The main grape varieties of this region are Furmint, Lipovina and Muscat blanc, which have specific sensory characteristics. This research work presents a strategy for the classification of three mentioned varieties of white wines using fluorescence spectroscopy with chemometrics. Emission and synchronous fluorescence spectra were obtained for bulk as well as diluted samples, principal component analysis (PCA) was applied for exploratory analysis and the scores of the selected PCs were used in linear discriminant analysis (LDA). For undiluted samples, the best PCA-LDA models based on either emission spectra excited at 370 nm or synchronous fluorescence spectra obtained at wavelength difference of 40 and 100 nm provided total correct classifications of 100, 100 and 93% for the calibration, validation and prediction steps, respectively. For diluted samples, the best PCA-LDA models (excitation at 280 nm; wavelength difference of 40 nm) again provided total correct classifications as mentioned above.
Keywords: Fluorescence; Linear discriminant analysis; Principal component analysis; Varietal classification; White wines.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Azcarate SM, de Araújo GA, Alcaraz MR, Ugulino de Araújo MC, Camiña JM, Goicoechea HC. Modeling excitation–emission fluorescence matrices with pattern recognition algorithms for classification of Argentine white wines according grape variety. Food Chem. 2015;184:214–219. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.081. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
