Emerging Roles of Long non-coding RNAs in The Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 32549757
- PMCID: PMC7294937
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.44420
Emerging Roles of Long non-coding RNAs in The Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
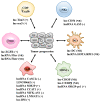
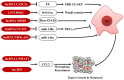
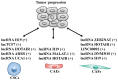
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a diverse class of longer than 200 nucleotides RNA transcripts that have limited protein coding capacity. LncRNAs display diverse cellular functions and widely participate in both physiological and pathophysiological processes. Aberrant expressions of lncRNAs are correlated with tumor progression, providing sound rationale for their targeting as attractive anti-tumor therapeutic strategies. Emerging evidences support that lncRNAs participate in tumor-stroma crosstalk and stimulate a distinctive and suitable tumor microenvironment (TME). The TME comprises several stromal cells such as cancer stem cells (CSCs), cancer-associated endothelial cells (CAEs), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and infiltrated immune cells, all of which are involved in the complicated crosstalk with tumor cells to affect tumor progression. In this review, we summarize the essential properties and functional roles of known lncRNAs in related to the TME to validate lncRNAs as potential biomarkers and promising anti-cancer targets.
Keywords: cancer-associated endothelial cells; cancer-associated fibroblasts; cancer-stem cells; immune cells; long non-coding RNA; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

