Mechanisms of offline motor learning at a microscale of seconds in large-scale crowdsourced data
- PMID: 32550003
- PMCID: PMC7272649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41539-020-0066-9
Mechanisms of offline motor learning at a microscale of seconds in large-scale crowdsourced data
Abstract
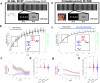
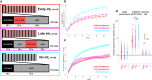
Performance improvements during early human motor skill learning are suggested to be driven by short periods of rest during practice, at the scale of seconds. To reveal the unknown mechanisms behind these "micro-offline" gains, we leveraged the sampling power offered by online crowdsourcing (cumulative N over all experiments = 951). First, we replicated the original in-lab findings, demonstrating generalizability to subjects learning the task in their daily living environment (N = 389). Second, we show that offline improvements during rest are equivalent when significantly shortening practice period duration, thus confirming that they are not a result of recovery from performance fatigue (N = 118). Third, retroactive interference immediately after each practice period reduced the learning rate relative to interference after passage of time (N = 373), indicating stabilization of the motor memory at a microscale of several seconds. Finally, we show that random termination of practice periods did not impact offline gains, ruling out a contribution of predictive motor slowing (N = 71). Altogether, these results demonstrate that micro-offline gains indicate rapid, within-seconds consolidation accounting for early skill learning.
Keywords: Consolidation; Human behaviour.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

