Current Management of Paediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
- PMID: 32550057
- PMCID: PMC7294900
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.8137
Current Management of Paediatric Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
Abstract
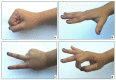
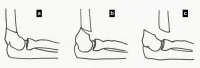
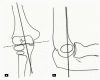
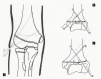
Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children are common and can be distressing injuries to the child, the parents and to the surgical team. Type 1 fractures are managed non-operatively, however displaced fractures (Types 2, 3 and 4) are usually managed surgically. Accurate and repetitive neuromuscular assessment is critical not just for medicolegal reasons but also to expedite management with different specialists if needed. The Rock, paper, scissor, OK technique is simple which is easily understood by most children. We discuss the current evidence with regards to pin diameter, number, pin configuration along with a simple algorithm on how to manage a child with a displaced supracondylar fracture with no pulse focussing mainly on the extension-type fracture.
Keywords: cubitus varus; elbow injury; elbow trauma; fracture in a child; humeral fracture; supracondylar humeral fracture.
Copyright © 2020, Shenoy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Fracture patterns in children. Analysis of 8,682 fractures with special reference to incidence, etiology and secular changes in a Swedish urban population 1950-1979. Landin LA. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6574687/?from_term=landin+la+1983&from_p.... Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1983;202:1–109. - PubMed
-
- Limb fracture pattern in different pediatric age groups: a study of 3,350 children. Cheng JC, Shen WY. https://journals.lww.com/jorthotrauma/Abstract/1993/02000/Limb_Fracture_.... J Orthop Trauma. 1993;7:15–22. - PubMed
-
- British Orthopaedic Association (BOA) standards for trauma and orthopaedics (BOASTs) [Apr;2020 ];British Orthopaedic Association Standards for Trauma. https://www.boa.ac.uk/standards-guidance/boasts.html 2014 11
-
- Etiology of supracondylar humerus fractures. Farnsworth CL, Silva PD, Mubarak SJ. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18:38–42. - PubMed
-
- Nerve injuries associated with pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis. Babal JC, Mehlman CT, Klein G. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30:253–263. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
