Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of contaminated mussels: A 2018 case report in Caparica (Portugal)
- PMID: 32550574
- PMCID: PMC7286109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2019.100017
Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of contaminated mussels: A 2018 case report in Caparica (Portugal)
Abstract
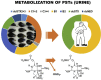
In Portugal, the potent paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) have appeared irregularly since the onset of a national monitoring program for marine biotoxins in 1986. In years where high contamination levels were attained in bivalves, sporadic cases of human poisonings have been recorded, as in 1994 and 2007. The reappearance of high contamination levels led to the appearance of new cases during the autumn of 2018. This study details toxin ingestion, symptomatology and toxin elimination and metabolization in the fluids of two patients, who ingested mussels from the Portuguese southwest coast and required hospitalization due to the severity of symptoms. Toxin elimination was confirmed by ELISA in plasma and urine samples. In mussel samples, the toxin profile obtained by HPLC-FLD displayed a wide diversity of toxins, typical of Gymnodinum catenatum ingestion. However, in the urine samples, the toxin profile was reduced to B1 and dcSTX. Abundant compounds in mussels having an O-sulphate at C11, such as C1+2 and dcGTX2+3, were absent in urine. In plasma, PSTs were not detected by HPLC-FLD. Calculated toxin ingestion, resulting from consumption of an estimated 200-g portion, was in the range of 104-120 μg STX eq./kg b. w.
Keywords: ELISA; HPLC; Human samples; Paralytic shellfish poisoning; Portugal; Saxitoxin; Seafood poisoning.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures






References
-
- Anon . AOAC International; Gaithersburg, MD, USA: 2005. AOAC Official Method 2005.06 Quantitative Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish Using Prechromatographic Oxidation and Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1980 of 31 October 2017 amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 2074/2005 as regards paralytic shellfish poison (PSP) detection method. Off.J.Eur.Union. 2017;L285:8–9.
-
- Artigas M.L., Vale P., Gomes S.S., Botelho M.J., Rodrigues S.M., Amorim A. Profiles of PSP toxins in shellfish from Portugal explained by carbamoylase activity. J. Chromatogr. A. 2007;1160(1–2):99–105. - PubMed
-
- Bolch C.J.S., de Salas M.F. A review of the molecular evidence for ballast water introduction of the toxic dinoflagellates Gymnodinium catenatum and the Alexandrium “tamarensis complex” to Australasia. Harmful Algae. 2007;6:465–485.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

