Optimization of the rat digit abduction score (DAS) assay: Evaluation of botulinum neurotoxin activity in the gastrocnemius lateralis, peronei, and extensor digitorum longus
- PMID: 32550584
- PMCID: PMC7285904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2020.100029
Optimization of the rat digit abduction score (DAS) assay: Evaluation of botulinum neurotoxin activity in the gastrocnemius lateralis, peronei, and extensor digitorum longus
Abstract
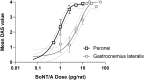
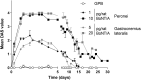
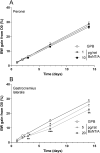
The mouse digit abduction score (DAS) assay is commonly used to measure muscle flaccidity-inducing effects of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) in vivo. Adapting the assay to rats has been challenging, as injection of onabotulinumtoxinA (onaBoNT-A) into the gastrocnemius muscle, as performed in mice, or into the tibialis anterior leads to sub-optimal sensitivity of the test (Broide et al., 2013). To optimize the experimental design of the rat DAS assay, we evaluated the effects of research-grade, purified, native BoNT serotype A1 (BoNT-A) in three muscles: the gastrocnemius lateralis, peronei, and extensor digitorum longus using female animals. Following injection, animals were tested daily for the digit abduction and body weight. BoNT-A caused dose-dependent inhibition of digit abduction when injected into the gastrocnemius lateralis or peronei. BoNT-A was six-fold more potent when injected into the peronei in comparison to the gastrocnemius lateralis. As injection of BoNT-A into the extensor digitorum longus muscle resulted in an all-or-none digit abduction response and therefore prevented calculation of the ED50, it was considered unsuitable for the rat DAS assay. At equipotent doses, peronei- and extensor digitorum longus-injected animals showed normal body weight gain, while those injected with BoNT-A into the gastrocnemius lateralis gained less weight in comparison to vehicle-treated controls. Thus, injecting the peronei muscles of female rats offers optimized conditions for evaluating the biological properties of BoNTs in the rat DAS assay; for assessing the potency, onset, and duration of action across natural and recombinant BoNT in a robust and reproducible manner.
Keywords: Botulinum neurotoxin type A; Digit abduction score; Extensor digitorum longus muscle; Gastrocnemius muscle; Peronei muscle.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
SC, CP, and MK are all employees of Ipsen Innovation, France.
Figures
References
-
- Adler M., Keller J., Sheridan R.E., Deshpande S.S. Persistence of botulinum neurotoxin A demonstrated by sequential administration of serotypes A and E in rat EDL muscle. Toxicon. 2001;39(2–3):233–243. - PubMed
-
- Aoki K.R. Preclinical update on BOTOX (botulinum toxin type A)-purified neurotoxin complex relative to other botulinum neurotoxin preparations. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999;6(Suppl. 4):S3–S10. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.1999.tb00032.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

