Role of Endoscopic Internal Maxillary Artery Ligation in Intractable Idiopathic Epistaxis
- PMID: 32551282
- PMCID: PMC7276470
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-020-01788-y
Role of Endoscopic Internal Maxillary Artery Ligation in Intractable Idiopathic Epistaxis
Abstract
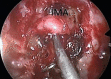
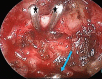
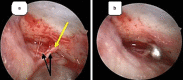
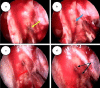
The protocols for managing intractable idiopathic epistaxis have evolved with advances in endoscopic techniques. Transnasal endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation (TESPAL) has been the treatment of choice for idiopathic intractable epistaxis. If TESPAL fails, transantral ligation of internal maxillary artery (IMA) used to be the dictum along with radiological interventions. Here we discuss about the role of endoscopic IMA ligation in cases of failed TESPALs. Retrospective study at a tertiary hospital was performed. 28 cases of intractable idiopathic epistaxis underwent TESPAL in our institution of which 2 cases had rebleed. We also had two referred cases of failed TESPALS. Of this 4 patients, three patients underwent endoscopic IMA ligation and one patient underwent selective embolisation. All the patients who underwent endoscopic IMA ligation for failed TESPAL had no further episodes of epistaxis. One patient who underwent selective embolization also had no further episodes of bleed but had transient facial pain and trismus. When TESPAL fails, endoscopic IMA ligation can be considered as an alternative procedure before resorting to embolization.
Keywords: Endoscopic internal maxillary artery (IMA) ligation; Intractable idiopathic epistaxis; Transnasal endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation (TESPAL).
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
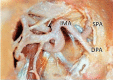

References
-
- Chandler JR, Serrins AJ. Transantral ligation of the internal maxillary artery for epistaxis. Laryngoscope. 1965;75:1151–1159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
