Synovial interlukin-6 affects apoptosis induction via nuclear factor kappa-B and fractalkine pathway during adjuvant arthritis
- PMID: 32551314
- PMCID: PMC7293817
- DOI: 10.34171/mjiri.34.25
Synovial interlukin-6 affects apoptosis induction via nuclear factor kappa-B and fractalkine pathway during adjuvant arthritis
Abstract
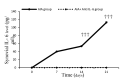
Background: Apoptosis disruptions play substantial roles in pathogenesis of arthritis and its symptoms. Cytokines and their intracellular signaling have pivotal roles in arthritis pathophysiology. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between synovial Interleukin-6 (IL-6), nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-ĸB), and fractalkine (FKN) in the changes of edema and apoptosis during adjuvantinduced knee arthritis. Methods: A total of 240 male Wistar rats were divided into different groups. Arthritis was evoked and the knee edema changes were evaluated by Vernier caliper. Synovial IL-6 was assayed by rat standard ELISA kit. Levels of NF-ĸB, fractalkine, and apoptotic indicators in the synovium were evaluated by Western blot method. Results were expressed as Mean± SEM. To analyze within-group variations, repeated measures ANOVA, followed by post hoc Tukey's test was used (SPSS, 16). Independent samples t test was used to designate significant differences in knee diameter, synovial level of IL-6, apoptotic markers, NF-ĸB, and FKN between groups. Significance level was set at P≤ 0.05. Results: The injection of Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA) caused intense knee edema (P< 0.001), which was reduced by implementing anti-IL-6 (P< 0.001), anti-FKN (P< 0.001), Inh-NF-ĸB (P< 0.001), and anti-FKN+ Inh NF-kB (P< 0.001). The results indicated elevated levels of apoptotic markers during the acute phase (P = 0.010), along with an increase in IL-6 (P< 0.001), NF-ĸB (P< 0.001), and FKN (P= 0.030). Although IL-6 (P< 0.001), NF-ĸB (P= 0.001), and FKN (P= 0.007) levels elevation continued during the chronic phase, the apoptosis markers decreased in this phase (P= 0.050). The findings revealed that Anti-IL-6 treatment during different phases of the study could change the synovial NF-ĸB and FKN. Conclusion: It seems that time-dependent variations in apoptotic markers level may be involved in pathogenesis of adjuvant-induced knee arthritis. In conclusion, synovial IL-6 through NF-ĸB- FKN pathway can play an important role in this process.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Apoptosis; Fractalkine; IL-6; Inflammation; NF-ĸB.
© 2020 Iran University of Medical Sciences.
References
-
- Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z. Apoptosis, autophagy, and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:2405–2419. - PubMed
-
- Amani H, Habibey R, Hajmiresmail SJ, Latifi Sh, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Akhavan O. Antioxidant nanomaterials in advanced diagnoses and treatments of ischemia reperfusion injuries. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:9452–9476. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Faustman D. Role of defective apoptosis in type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune diseases. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2003;58:131–153. - PubMed
-
- William-Vandivier R, Henson PM, Douglas IS. The impact of failed apoptotic cell removal (Efferocytosis) on chronic inflammatory lung disease. Chest. 2006;129:1673–1682. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous