Non-invasive Brain Delivery and Efficacy of BDNF in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice as a Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32551362
- PMCID: PMC7302105
- DOI: 10.18103/mra.v8i2.2043
Non-invasive Brain Delivery and Efficacy of BDNF in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice as a Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
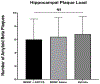
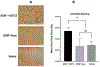
Neurotrophic factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF) have been demonstrated for their potential as a neuroregenerative treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Unfortunately, most proteins cannot be effectively delivered into the brain from the blood stream due to the presence of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). In this study, we delivered BDNF using ADTC5 as BBB modulator (BBBM) into the brains of transgenic APP/PS1 mice, a mouse model for AD. As controls, two groups of APP/PS1 mice were treated with BDNF alone and vehicle, respectively. All three groups were subjected to behavioral/cognitive assessments in Y-maze and novel object recognition (NOR) tests as well as evaluation of the brain markers activated by BDNF. The results showed that BDNF + ADTC5 group performed significantly better in both the Y-maze and NOR assessments compared to mice that received BDNF alone or vehicle. In addition, significant upregulations of NG2 receptors as well as EGR1 and ARC mRNA transcripts were observed in the brain cortex of mice treated with BDNF + ADTC5, further indicating the efficacy of delivered BDNF in the brain. There were high plaque loads in all groups of mice, suggesting no influence of BDNF on the plaque formation. In summary, ADTC5 can deliver BDNF into the brains of APP/PS1 mice and the activity of BDNF in improving cognitive function was likely due to improvement in synaptic plasticity via NG2 glia cells and not by reducing the plaque load.
Keywords: APP/PS1 mice; Alzheimer’s Diseas; BBB modulation; BDNF; Blood-Brain Barrier; Brain delivery; neuroregeneration.
Figures
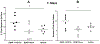
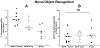

Similar articles
-
Noninvasive Brain Delivery and Efficacy of BDNF to Stimulate Neuroregeneration and Suppression of Disease Relapse in EAE Mice.Mol Pharm. 2020 Feb 3;17(2):404-416. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00644. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31846344 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of an additional chronic BDNF reduction on learning performance in an Alzheimer mouse model.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Mar 20;9:58. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00058. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852506 Free PMC article.
-
Lamotrigine attenuates deficits in synaptic plasticity and accumulation of amyloid plaques in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Dec;35(12):2713-2725. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 25044076
-
Using mice to model Alzheimer's dementia: an overview of the clinical disease and the preclinical behavioral changes in 10 mouse models.Front Genet. 2014 Apr 23;5:88. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00088. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24795750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of Neuroregenerative Proteins to the Brain for Treatments of Neurodegenerative Brain Diseases.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 10;14(11):1456. doi: 10.3390/life14111456. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39598254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the pathogenesis of stress-related brain diseases.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Sep 14;16:1247422. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1247422. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37781095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of the blood-brain barrier modulation by cadherin peptides.Explor Drug Sci. 2024;2(3):322-338. doi: 10.37349/eds.2024.00049. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Explor Drug Sci. 2024. PMID: 39118806 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Antibody Exposure in the Central Nervous System: Mechanisms of Uptake, Clearance, and Strategies for Improved Brain Delivery.J Nanotheranostics. 2023 Dec;4(4):463-479. doi: 10.3390/jnt4040020. Epub 2023 Oct 2. J Nanotheranostics. 2023. PMID: 39897432 Free PMC article.
-
Can exercise benefits be harnessed with drugs? A new way to combat neurodegenerative diseases by boosting neurogenesis.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Jul 25;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00428-7. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39049102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise mimetics: a novel strategy to combat neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 2;21(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03031-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38308368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Courtney C, Farrell D, Gray R, Hills R, Lynch L, Sellwood E, Edwards S, Hardyman W, Raftery J, Crome P, Lendon C, Shaw H, Bentham P, Group ADC, Long-term donepezil treatment in 565 patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD2000): randomised double-blind trial. Lancet 2004;363:2105–15. - PubMed
-
- Loy C, Schneider L, Galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: 1996; Vol. 16.
-
- Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ, Memantine Study G., Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1333–41. - PubMed
-
- Prasher VP, Review of donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine and memantine for the treatment of dementia in Alzheimer’s disease in adults with Down syndrome:implications for the intellectual disability population. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2004;19:509–15. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
