In vivo and in vitro evaluation of pharmacological activities of Adenia trilobata (Roxb.)
- PMID: 32551370
- PMCID: PMC7292905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100772
In vivo and in vitro evaluation of pharmacological activities of Adenia trilobata (Roxb.)
Abstract
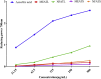
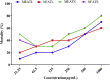
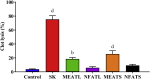
Adenia trilobata, locally known as akandaphal in Bangladesh, has some traditional uses. Leaves and stems extracted with pure methanol (MEATL, MEATS) and fractioned by n-hexane (NFATL, NFATS), which was subjected to qualitative phytochemical analysis. The qualitative phytochemical analysis of four extracts showed the presence of secondary metabolites such as alkaloid, carbohydrate, glycosides, flavonoids, phenols, flavonol, and saponins. All four extracts of A. trilobata, exhibited a strong antioxidant activity while a moderately (MEATS = 328 μg/mL) to weakly toxic (NFATL = 616.85 μg/mL) LC50 observed in brine shrimp lethality bioassay. In thrombolytic test, MEATL (18.54 ± 2.18%; P < 0.01) and MEATS (25.58 ± 4.76%; P < 0.0001) showed significant percentage of clot lysis in human blood. The in vivo analgesic activity carried by acetic acid test and formalin test, while the antidiarrheal activity assayed by two standard methods e.g., castor oil-induced diarrhea and castor oil-induced gastrointestinal motility. Both, in vivo model, showed an extremely significant (P < 0.0001) dose-dependent manner percentage of inhibition in comparison to the control group. Present results suggested, A. trilobata could be a potential source for antioxidative, cytotoxic, thrombolytic, analgesic, antidiarrheal agents which require further study to identify the mechanism of A. trilobata.
Keywords: A. trilobata; A. trilobata, Adenia trilobata; ANOVA, Analysis of variance; Analgesic activity; Antidiarrheal; Antioxidant; Cytotoxic; DPPH, 1,1-diphenyl, 2-picryl hydrazyl; FCR, Folin-Ciocalteu reagent; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; IP, intraperitoneal; LC50, 50% lethal concentration; OS, oxidative stress; SEM, standard error mean; Thrombolytic; UV, ultra-violet; b.w., body weight.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Festa F., Aglitti T., Duranti G., Ricordy R., Perticone P., Cozzi R. Strong antioxidant activity of ellagic acid in mammalian cells in vitro revealed by the comet assay. Anticancer Res. 2001;21(6A):3903–3908. - PubMed
-
- Nicolini F.A., Nichols W.W., Mehta J.L., Saldeen T.G., Schofield R., Ross M., Player D.W., Pohl G.B., Mattsson C. Sustained reflow in dogs with coronary thrombosis with K2P, a novel mutant of tissue-plasminogen activator. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1992;20(1):228–235. - PubMed
-
- Milind P., Monu Y. Laboratory models for screening analgesics. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2013;4:15–19.
-
- Kumar M., Shek A., Akbar Z. A review on analgesic: from natural sources. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 2010;1:95–100.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

