Jettison-MS of Nucleic Acid Species
- PMID: 32551641
- PMCID: PMC12392698
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.0c00084
Jettison-MS of Nucleic Acid Species
Abstract
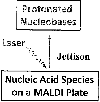
While MALDI-MS of intact genomic DNA is unheard of, actually many DNA adducts can be detected in this way under certain MALDI conditions: relatively high molar ratio of DNA nucleobases to matrix (0.01 to 0.3), hot matrix (CCA), and high laser fluence. This is because many DNA adducts create "bubbles" on dsDNA (disruption of base pairing), making it easier for these adducts as modified nucleobases to be jettisoned by the laser-derived energy of MALDI (jettison mass spectrometry or JeMS). The method also works for other nucleic acid species, namely nucleobases, nucleosides, nucleotides, and RNA. Examples of what we have detected in this way are as follows: methyladenine in E. coli DNA, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in human brain DNA, melphalan-adenine in leukocyte DNA from patients on corresponding chemotherapy, wybutosine in tRNA, benzyl DNA adducts in E. coli cell culture treated with benzyl bromide, and various DNA adducts formed in test tube exposure experiments with calf thymus DNA. Noteworthy, in the chemotherapy study, principle component analysis of the data encourages the hypothesis that patient DNA undergoes much more damage than just melphalan adducts. Overall, our work leads to the preliminary generalization that about 5 fmol of a nucleobase deficient in base pairing, and present in a MALDI spot, will be detected by JeMS (on the equipment that we used), irrespective of the type of nucleic acid species which houses it, as long as the nucleobase is relatively basic such as A, C, or G.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Stemmler EA; Buchanan MV; Hurst GB; Hettich RL Structural characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon dihydrodiol epoxide DNA adducts using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 1994, 66, 1274–85. - PubMed
-
- Stemmler EA; Buchanan MV; Hurst GB; Hettich RL Analysis of modified oligonucleotides by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 1995, 67, 2924–30. - PubMed
-
- van den Boom D; Berkenkamp S MALDI-MS of Nucleic Acids and Practical Implementations in Genomics and Genetics. In MALDI MS: A Practical Guide to Instrumentation, Methods and Applications; Hillenkamp F, Peter-Katalinic J, Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007.
-
- Moschel RC; Hudgins WR; Dipple A Selectivity in Nucleoside Alkylation and Aralkylation in Relation to Chemical Carcinogenesis. J. Org. Chem 1979, 44, 3324–3328.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

