Genome-Wide Association Study: Functional Variant rs2076295 Regulates Desmoplakin Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 32551799
- PMCID: PMC7605184
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201910-1958OC
Genome-Wide Association Study: Functional Variant rs2076295 Regulates Desmoplakin Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells
Abstract
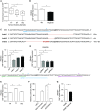
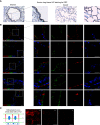
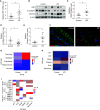
Rationale: Genetic association studies have identified rs2076295 in association with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We hypothesized that rs2076295 is the functional variant regulating DSP (desmoplakin) expression in human bronchial epithelial cells, and DSP regulates extracellular matrix-related gene expression and cell migration, which is relevant to IPF development.Objectives: To determine whether rs2076295 regulates DSP expression and the function of DSP in airway epithelial cells.Methods: Using CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)/Cas9 editing (including regional deletion, indel, CRISPR interference, and single-base editing), we modified rs2076295 and measured DSP expression in edited 16HBE14o- and primary airway epithelial cells. Cellular integrity, migration, and genome-wide gene expression changes were examined in 16HBE14o- single colonies with DSP knockout. The expression of DSP and its relevant matrix genes was measured by quantitative PCR and also analyzed in single-cell RNA-sequencing data from control and IPF lungs.Measurements and Main Results:DSP is expressed predominantly in bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells, with reduced expression in alveolar epithelial cells in IPF lungs. The deletion of the DNA region-spanning rs2076295 led to reduced expression of DSP, and the edited rs2076295GG 16HBE14o- line has lower expression of DSP than the rs2076295TT lines. Knockout of DSP in 16HBE14o- cells decreased transepithelial resistance but increased cell migration, with increased expression of extracellular matrix-related genes, including MMP7 and MMP9. Silencing of MMP7 and MMP9 abolished increased migration in DSP-knockout cells.Conclusions: rs2076295 regulates DSP expression in human airway epithelial cells. The loss of DSP enhances extracellular matrix-related gene expression and promotes cell migration, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of IPF.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9 genome-editing; DSP; bronchial epithelial cells; cell migration; rs2076295.
Figures



Comment in
-
Desmoplakin: An Important Player in Aging Lung Disease.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Nov 1;202(9):1201-1202. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202006-2457ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32716632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Desmoplakin Variants Are Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 May 15;193(10):1151-60. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201509-1863OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016. PMID: 26669357 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing Mechanoinductive DSP Expression by CRISPR/dCas9-mediated Epigenome Editing.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Sep 1;198(5):599-609. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201711-2242OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29924937 Free PMC article.
-
DSP rs2076295 variants influence nintedanib and pirfenidone outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a pilot study.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;15:17534666211042529. doi: 10.1177/17534666211042529. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 34515605 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Airway Epithelial Cell Gene Editing Using CRISPR-Cas9.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1706:267-292. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423804 Review.
-
Trade-offs in aging lung diseases: a review on shared but opposite genetic risk variants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018 May;24(3):309-317. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000476. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29517586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Diminution of R-Loops Generated by LncRNA DSP-AS1 Inhibits DSP Gene Transcription to Impede the Re-Epithelialization During Diabetic Wound Healing.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(12):e2406021. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406021. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39921255 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Metagenomes and Host Transcriptomes Reveal the Dynamic Changes of Rumen Gene Expression, Microbial Colonization and Co-Regulation of Mineral Element Metabolism in Yaks from Birth to Adulthood.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;14(9):1365. doi: 10.3390/ani14091365. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731369 Free PMC article.
-
An Airway-Centric View of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Aug 15;206(4):410-416. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2219PP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35446237 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Colocalization of Gene Expression and DNA Methylation with Genetic Risk Variants Supports Functional Roles of MUC5B and DSP in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Nov 15;206(10):1259-1270. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202110-2308OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35816432 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Update on Pathogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 19;12:797292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.797292. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35126134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2017;389:1941–1952. - PubMed
-
- Martinez FJ, Collard HR, Pardo A, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Selman M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17074. - PubMed
-
- Ley B, Collard HR, King TE., Jr Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Xaubet A, Ancochea J, Molina-Molina M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [in English, Spanish] Med Clin (Barc) 2017;148:170–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

