Prone Positioning of Nonintubated Patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32551807
- PMCID: PMC7427393
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1331LE
Prone Positioning of Nonintubated Patients with COVID-19
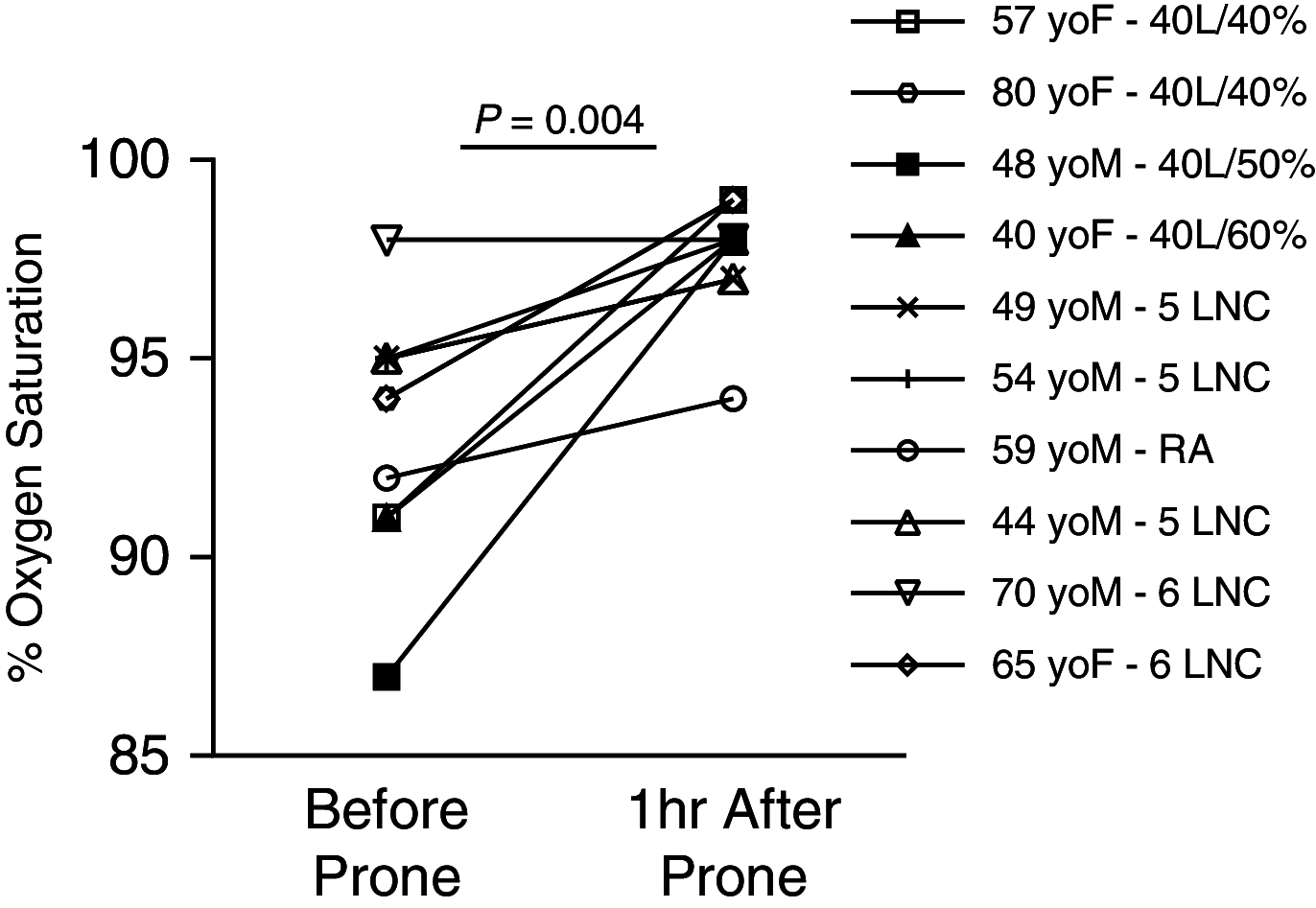
Figures

References
-
- Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard J-C, Beuret P, Gacouin A, Boulain T, et al. PROSEVA Study Group. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2159–2168. - PubMed
-
- Valter C, Christensen AM, Tollund C, Schønemann NK. Response to the prone position in spontaneously breathing patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003;47:416–418. - PubMed
-
- Scaravilli V, Grasselli G, Castagna L, Zanella A, Isgrò S, Lucchini A, et al. Prone positioning improves oxygenation in spontaneously breathing nonintubated patients with hypoxemic acute respiratory failure: a retrospective study. J Crit Care. 2015;30:1390–1394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

