From "Infodemics" to Health Promotion: A Novel Framework for the Role of Social Media in Public Health
- PMID: 32552021
- PMCID: PMC7427212
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2020.305746
From "Infodemics" to Health Promotion: A Novel Framework for the Role of Social Media in Public Health
Abstract
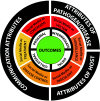
Despite the ubiquity of health-related communications via social media, no consensus has emerged on whether this medium, on balance, jeopardizes or promotes public health. During the COVID-19 pandemic, social media has been described as the source of a toxic "infodemic" or a valuable tool for public health. No conceptual model exists for examining the roles that social media can play with respect to population health.We present a novel framework to guide the investigation and assessment of the effects of social media on public health: the SPHERE (Social media and Public Health Epidemic and REsponse) continuum. This model illustrates the functions of social media across the epidemic-response continuum, ranging across contagion, vector, surveillance, inoculant, disease control, and treatment.We also describe attributes of the communications, diseases and pathogens, and hosts that influence whether certain functions dominate over others. Finally, we describe a comprehensive set of outcomes relevant to the evaluation of the effects of social media on the public's health.
Figures
Comment in
-
Misinformation.Am J Public Health. 2021 Feb;111(2):e3-e4. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2020.306056. Am J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33439720 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Schillinger and Ramírez Respond.Am J Public Health. 2021 Feb;111(2):e4-e5. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2020.306058. Am J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33439723 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pew Research Center. Social media fact sheet. 2019. Available at: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/fact-sheet/social-media. Accessed March 18, 2020.
-
- Sun M, Yang L, Chen W et al. Current status of official WeChat accounts for public health education. J Public Health (Oxf). 2020 Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources