Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells on a Chip: A Self-Contained, Accessible, Pipette-less iPSC Culturing and Differentiation Kit
- PMID: 32552316
- PMCID: PMC10843275
- DOI: 10.1177/2472630320921173
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells on a Chip: A Self-Contained, Accessible, Pipette-less iPSC Culturing and Differentiation Kit
Abstract
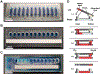
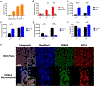
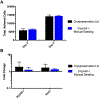
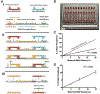
Over the past decade, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have become a major focus of stem cell and developmental biology research, offering researchers a clinically relevant source of cells that are amenable to genetic engineering approaches. Though stem cells are promising for both research and commercial endeavors, iPSC-based assays require tedious protocols that include complex treatments, expensive reagents, and specialized equipment that limit their integration into academic curricula and cell biology research groups. Expanding on existing Kit-On-A-Lid-Assay (KOALA) technologies, we have developed a self-contained, injection molded, pipette-less iPSC culture and differentiation platform that significantly reduces associated costs and labor of stem cell maintenance and differentiation. The KOALA kit offers users the full range of iPSC culture necessities, including cell cryopreservation, media exchanges, differentiation, endpoint analysis, and a new capability, cell passaging. Using the KOALA kit, we were able to culture ~20,000 iPSCs per microchannel for at least 7 days, while maintaining stable expression of stemness markers (SSEA4 and Oct4) and normal iPSC phenotype. We also adapted protocols for differentiating iPSCs into neuroepithelial cells, cardiomyocytes, and definitive endodermal cells, a cell type from each germ layer of human development.
Keywords: cell culture incubators; lab-on-a-chip; microfluidics; microtechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: David J. Beebe holds equity in Bellbrook Labs LLC, Tasso Inc., Salus Discovery LLC, LynxBiosciences Inc., Turba LLC, Stacks to the Future LLC, and Onexio Biosystems LLC. David J. Guckenberger holds equity in Tasso Inc. and Salus Discovery LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced structural maturation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes under a controlled microenvironment in a microfluidic system.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jan 15;102:273-286. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.11.044. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31778832
-
Effect of human donor cell source on differentiation and function of cardiac induced pluripotent stem cells.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 5;64(5):436-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.056. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25082575 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Stability and Differentiation Potential of Cryopreserved cGMP-Compliant Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 23;21(1):108. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010108. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31877913 Free PMC article.
-
A Concise Review on Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Personalized Regenerative Medicine.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Jun;17(3):748-776. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10061-2. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 33098306 Review.
-
Techniques for the induction of human pluripotent stem cell differentiation towards cardiomyocytes.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017 May;11(5):1658-1674. doi: 10.1002/term.2117. Epub 2016 Jan 17. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017. PMID: 26777594 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Disease Modeling and 3D Model Construction: Focus on Osteoarthritis.Cells. 2021 Nov 5;10(11):3032. doi: 10.3390/cells10113032. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An WF, Tolliday N. Cell-Based Assays for High-Throughput Screening. Mol. Biotechnol. 2010, 45, 180–186 - PubMed
-
- Evans Anderson HJ CRISPR in the Undergraduate Classroom: A CURE. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 589.6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
