Comparisons of quality of life between patients underwent peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32552800
- PMCID: PMC7302145
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-020-01449-2
Comparisons of quality of life between patients underwent peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) leads to renal replacement therapy and certainly has an impact on patients' health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study aimed to review and compare the HRQoL between peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD) patients using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), EuroQoL-5-dimension (EQ-5D) and the Kidney Disease Quality of Life Instrument (KDQOL).
Methodology: Systematic review was conducted by identify relevant studies through MEDLINE and SCOPUS up to April 2017. Studies were eligible with following criteria: studied in ESRD patients, compare any pair of renal replacement modalities, and reported HRQoL. The unstandardized mean differences (USMD) of HRQoL among modalities were calculated and pooled using a random-effect models if heterogeneity was present, otherwise a fixed-effect model was applied.
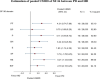
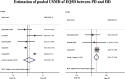
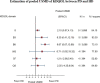
Results: A total of twenty-one studies were included with 29,000 participants. Of them, mean age and percent male were 48.1 years and 45.1, respectively. The pooled USMD (95% CI) of SF-36 between PD and HD (base) were 1.86 (0.47, 3.24) and 0.42 (- 1.99, 2.82) for mental component and physical component summary scores, respectively. For EQ-5D, the pooled USMD of utility and visual analogue scale (VAS) score were 0.02 (- 0.06, 0.10) and 3.56 (1.73, 5.39), respectively. The pooled USMD of KDQOL were 9.67 (5.67, 13.68), 6.71 (- 5.92, 19.32) 6.30 (- 0.41, 12.18), 2.35 (- 4.35, 9.04), 2.10 (0.07, 4.13), and 1.21 (- 2.98, 5.40) for burden of kidney disease, work status, effects of kidney disease, quality of social interaction, symptoms, and cognitive function.
Conclusion: Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 5 or ESRD treated with PD had better generic HRQoL measured by SF-36 and EQ-5D than HD patients. In addition, PD had higher specific HRQoL by KDQOL than HD patients in subdomain of physical functioning, role limitations due to emotional problems, effects and burden of kidney disease.
Keywords: EQ-5D; Health-related quality of life; Hemodialysis; KDQOL; Peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Altunoglu A, Yavuz D, Canoz MB, et al. Relationship between inflammation and sex hormone profile in female patients receiving different types of renal replacement therapy. Transplant Proc. 2014;46(5):1585–1590. - PubMed
-
- Kostro JZ, Hellmann A, Kobiela J, et al. Quality of life after kidney transplantation: a prospective study. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(1):50–54. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs AZ, Molnar MZ, Szeifert L, et al. Sleep disorders, depressive symptoms and health-related quality of life--a cross-sectional comparison between kidney transplant recipients and waitlisted patients on maintenance dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(3):1058–1065. - PubMed
-
- Kalender B, Ozdemir AC, Dervisoglu E, et al. Quality of life in chronic kidney disease: effects of treatment modality, depression, malnutrition and inflammation. Int J Clin Pract. 2007;61(4):569–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous