KLF4 defines the efficacy of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, erlotinib, in triple-negative breast cancer cells by repressing the EGFR gene
- PMID: 32552913
- PMCID: PMC7301986
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-020-01305-7
KLF4 defines the efficacy of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, erlotinib, in triple-negative breast cancer cells by repressing the EGFR gene
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is characterized by high rates of recurrence and poor overall survival. This is due, in part, to a deficiency of targeted therapies, making it essential to identify therapeutically targetable driver pathways of this disease. While epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is expressed in 60% of TNBCs and drives disease progression, attempts to inhibit EGFR in unselected TNBC patients have had a marginal impact on outcomes. Hence, we sought to identify the mechanisms that dictate EGFR expression and inhibitor response to provide a path for improving the utility of these drugs. In this regard, the majority of TNBCs express low levels of the transcription factor, Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), while a small subset is associated with high expression. KLF4 and EGFR have also been reported to have opposing actions in TNBC. Thus, we tested whether KLF4 controls the expression of EGFR and cellular response to its pharmacological inhibition.
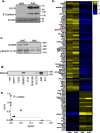
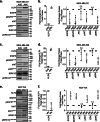
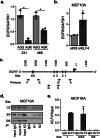
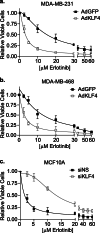
Methods: KLF4 was transiently overexpressed in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells or silenced in MCF10A cells. Migration and invasion were assessed using modified Boyden chamber assays, and proliferation was measured by EdU incorporation. Candidate downstream targets of KLF4, including EGFR, were identified using reverse phase protein arrays of MDA-MB-231 cells following enforced KLF4 expression. The ability of KLF4 to suppress EGFR gene and protein expression and downstream signaling was assessed by RT-PCR and western blot, respectively. ChIP-PCR confirmed KLF4 binding to the EGFR promoter. Response to erlotinib in the context of KLF4 overexpression or silencing was assessed using cell number and dose-response curves.
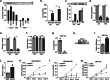
Results: We report that KLF4 is a major determinant of EGFR expression and activity in TNBC cells. KLF4 represses transcription of the EGFR gene, leading to reduced levels of total EGFR, its activated/phosphorylated form (pEGFR), and its downstream signaling intermediates. Moreover, KLF4 suppression of EGFR is a necessary intermediary step for KLF4 to inhibit aggressive TNBC phenotypes. Most importantly, KLF4 dictates the sensitivity of TNBC cells to erlotinib, an FDA-approved inhibitor of EGFR.
Conclusions: KLF4 is a major regulator of the efficacy of EGFR inhibitors in TNBC cells that may underlie the variable effectiveness of such drugs in patients.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); Erlotinib; Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4); Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of osteopontin as a predictive biomarker for anti-EGFR therapy in triple-negative breast cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Aug;22(8):727-734. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1502272. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 30025479
-
Excellent effects and possible mechanisms of action of a new antibody-drug conjugate against EGFR-positive triple-negative breast cancer.Mil Med Res. 2021 Dec 9;8(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00358-9. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34879870 Free PMC article.
-
A kinase inhibitor screen identifies a dual cdc7/CDK9 inhibitor to sensitise triple-negative breast cancer to EGFR-targeted therapy.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 1;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1161-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31262335 Free PMC article.
-
P53 mutations in triple negative breast cancer upregulate endosomal recycling of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) increasing its oncogenic potency.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Nov;88(2):284-92. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23755891 Review.
-
Small Molecule Therapeutics in the Pipeline Targeting for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Origin, Challenges, Opportunities, and Mechanisms of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 6;25(11):6285. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116285. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A recent development of new therapeutic agents and novel drug targets for cancer treatment.SAGE Open Med. 2021 Dec 23;9:20503121211067083. doi: 10.1177/20503121211067083. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med. 2021. PMID: 34992782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDC6 may serve as an indicator of lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and progression based on TCGA and GEO data mining and experimental analyses.Oncol Rep. 2024 Feb;51(2):35. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8694. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38186304 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal targeting and its potential clinical application.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Oct;12(10):2385-2402. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01087-1. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34973131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic effects of combined cisplatin and Clinacanthus nutans extract on triple negative breast cancer cells.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023 Apr 15;18(6):1220-1236. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2023.04.003. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37250812 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Discoveries on the Involvement of Krüppel-Like Factor 4 in the Most Common Cancer Types.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 22;21(22):8843. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228843. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA, Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California Cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109:1721–1728. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22618. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

