Drugs acting on renin angiotensin system and use in ill patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32553503
- PMCID: PMC7238972
- DOI: 10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.009
Drugs acting on renin angiotensin system and use in ill patients with COVID-19
Abstract
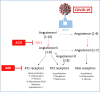
Some concerns about the prescription of drugs acting on the renin-angiotensin system (angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE1) inhibitors, ACEi; angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers, ARB) have emerged due to SARS COV2 and COVID-19 pandemic. These very legitimate questions are directly the consequence of the recent recognition of the fundamental role of ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) in COVID-19 infection. Indeed, SARS COV2 utilizes ACE2 as a membrane receptor to enter target cells. Consequently, the putative impact of drugs modulating the renin-angiotensin system on the risk of developing severe or fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome in case of COVID-19 infection emerged. As a membrane-bound enzyme (carboxypeptidase), ACE2 inactivates angiotensin II and therefore physiologically counters its effects. Due to a different structure compared with ACE1, ACE2 is insensitive to ACEIs. In vitro, both ARBs and ACEi appear able to upregulate ACE2 tissue expression and activity but these results were not confirmed in Humans. The exact impact of both ARBs and ACEis on COVID-19 infection is definitively known and preliminary results are even in favor of a protective role confers by these drugs. Due to the crucial role of ACE2, some groups support the hypothesis that a modulation of ACE2 expression could represent a valuable therapeutic target could confer protective properties against inflammatory tissue damage in COVID-19 infection. So, studies are currently ongoing to test the impact of elevated ACE2 membrane expression, administration of ARB and infusion of soluble ACE2. In summary, based on the currently available evidences and as recommended by several medical societies, ACEi or ARB should not be systematically discontinued because to date no safety signal was raised with the use of these drugs.
Keywords: Arterial hypertension; Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Copyright © 2020 Société française de pharmacologie et de thérapeutique. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Donoghue M., Hsieh F., Baronas E., Godbout K., Gosselin M., Stagliano N. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res. 2000;87(5):E1–E9. - PubMed
-
- Tipnis S.R., Hooper N.M., Hyde R., Karran E., Christie G., Turner A.J. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(43):33238–33243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous