Characteristics of circular RNAs generated by human Survival Motor Neuron genes
- PMID: 32553550
- PMCID: PMC7387165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109696
Characteristics of circular RNAs generated by human Survival Motor Neuron genes
Abstract
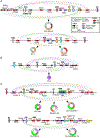
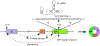
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) belong to a diverse class of stable RNAs expressed in all cell types. Their proposed functions include sponging of microRNAs (miRNAs), sequestration and trafficking of proteins, assembly of multimeric complexes, production of peptides, and regulation of transcription. Backsplicing due to RNA structures formed by an exceptionally high number of Alu repeats lead to the production of a vast repertoire of circRNAs by human Survival Motor Neuron genes, SMN1 and SMN2, that code for SMN, an essential multifunctional protein. Low levels of SMN due to deletion or mutation of SMN1 result in spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a major genetic disease of infants and children. Mild SMA is also recorded in adult population, expanding the spectrum of the disease. Here we review SMN circRNAs with respect to their biogenesis, sequence features, and potential functions. We also discuss how SMN circRNAs could be exploited for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: Alu elements; Backsplicing; Spinal muscular atrophy, SMA; Survival motor neuron, SMN; circRNA; microRNA.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

